How Long Do Cannabis Seeds Take To Sprout?

Growing cannabis can be a rewarding experience, but it requires patience and a good understanding of the plant’s life cycle. One of the first stages in this cycle is the germination of seeds. If you’re new to cannabis cultivation, you might be wondering, “How long do cannabis seeds take to sprout?” This blog post aims to answer that question in detail, guiding you through the germination process, factors that influence it, and tips for successful sprouting.
Introduction to Cannabis Germination
Germination is the first step in growing a cannabis plant. It’s the process where a seed transforms into a young seedling, ready to be planted and nurtured. This process is vital for the plant’s lifecycle and sets the foundation for its growth. Understanding how long this process takes and the factors that affect it is crucial for any grower aiming for a successful harvest. By mastering the germination process, you can significantly increase your chances of growing healthy and robust cannabis plants.
The Germination Process Explained
Cannabis seeds typically take between 24 hours to 7 days to sprout, depending on various conditions. Germination involves several stages, beginning with the seed absorbing water, followed by the activation of its metabolic processes, and ending with the emergence of the radicle (the first root). During this process, the seed undergoes significant changes:
- Water Absorption: The seed absorbs water, causing it to swell and the outer shell to crack.
- Metabolic Activation: Once water is absorbed, the seed’s metabolic activities begin, initiating growth.
- Radicle Emergence: The first root, or radicle, emerges, anchoring the plant and starting nutrient absorption.
- Shoot Development: The shoot, or plumule, pushes upwards, breaking through the soil to begin photosynthesis.
Factors Influencing Germination Time
Seed Quality
- Viability: Fresh, healthy seeds are more likely to germinate quickly, while old or damaged seeds may have reduced germination rates.
- Strain: Different cannabis strains can have varying germination times. Some strains naturally germinate faster than others.
- Storage: Seeds stored in optimal conditions (cool, dark, and dry) tend to sprout faster. Improper storage can damage seeds and hinder germination.
Environmental Conditions
- Temperature: Ideal temperatures range between 70-85°F (21-29°C). Temperatures outside this range can slow germination or prevent it entirely.
- Humidity: High humidity levels help seeds absorb water and initiate germination. Consistent moisture is crucial for the seed’s metabolic processes.
- Light: While light isn’t necessary for germination, it becomes crucial once the seedling emerges. Light helps the young plant begin photosynthesis and grow stronger.
Germination Method
- Paper Towel Method: Known for its effectiveness and ease, this method involves placing seeds between moist paper towels and keeping them in a warm, dark place.
- Direct Soil Planting: Mimics natural conditions but may take longer for the seeds to sprout as they need to penetrate the soil.
- Water Glass Method: Quick and simple, this method involves soaking seeds in water until they crack open and the radicle emerges.
- Rockwool Cubes: These cubes are common in hydroponic systems. They retain moisture well and provide a sterile environment for seeds to germinate.
Common Germination Methods
Paper Towel Method
- Preparation: Moisten a paper towel and place the seeds on it. Fold the towel over the seeds and place it in a container.
- Environment: Keep the towel in a warm, dark place, such as a cupboard or drawer.
- Monitoring: Check daily and ensure the towel remains moist. Add water if necessary.
- Transplantation: Once the radicle appears, move the seeds to the soil. Handle them gently to avoid damaging the delicate root.
Direct Soil Planting
- Soil Preparation: Use a light, well-draining soil. Avoid heavy soils that retain too much water.
- Planting: Place the seeds about 1/4 inch deep in the soil. Cover lightly and water gently.
- Watering: Keep the soil moist but not waterlogged. Overwatering can suffocate the seeds.
- Emergence: Seeds typically sprout within 7 days. Once the seedlings emerge, ensure they receive adequate light.
Water Glass Method
- Preparation: Fill a glass with water and drop the seeds in. Let them soak for 24-48 hours.
- Observation: Seeds that sink are more likely to germinate. Floating seeds may be less viable.
- Transfer: Once the radicle appears, move to soil or another medium. Be gentle to avoid damaging the emerging root.
Rockwool Cubes
- Soaking: Pre-soak the cubes in water with a pH of 5.5 to ensure they are adequately moist.
- Placement: Insert the seeds into the cubes. Place the cubes in a tray and cover with a dome to maintain humidity.
- Environment: Keep in a warm, humid area. A heat mat can help maintain a consistent temperature.
- Transplantation: Once sprouted, move to the growing medium. Rockwool cubes can be transplanted directly into hydroponic systems or soil.
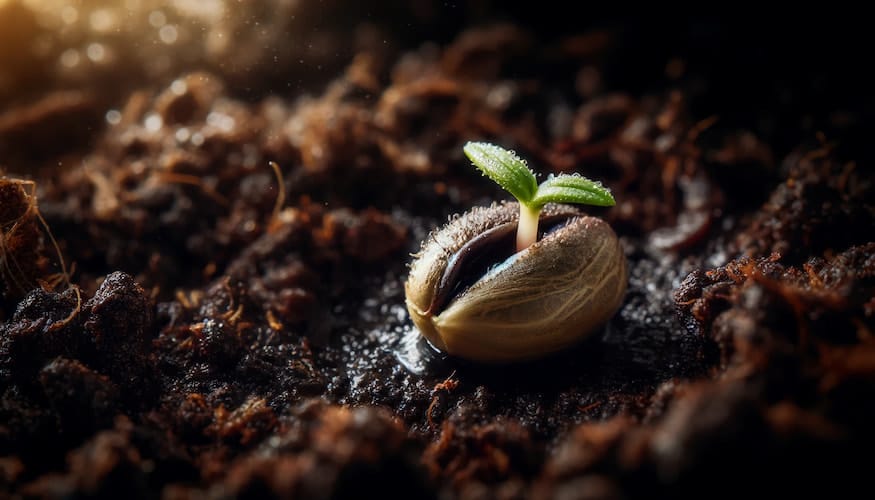

Stages of Cannabis Seed Germination
Imbibition
The germination of cannabis seeds involves several distinct stages, each crucial for the successful development of a healthy plant. The first stage is known as imbibition, where the seed begins to absorb water. This absorption causes the seed to swell, which eventually leads to the breaking of the outer shell. This initial stage can take a few hours to a couple of days, depending on the seed’s initial moisture content and the environmental conditions. The absorption of water is critical as it activates the seed’s metabolic processes, initiating the transition from a dormant state to active growth.
Radicle Emergence
Following imbibition is the emergence of the radicle, which is the first root to develop from the seed. The radicle’s appearance is a vital milestone in germination, as it anchors the plant into the soil and starts to absorb nutrients necessary for further growth. Typically, the radicle emerges within two to four days after the seed begins the imbibition process. This stage is crucial as it lays the foundation for the plant’s root system, which will support its nutritional needs throughout its life cycle.
Seedling Development
The final stage of germination is the development of the seedling. During this phase, the shoot, or plumule, begins to grow upwards, eventually breaking through the soil surface. This shoot will develop into the plant’s main stem and leaves. The first set of true leaves, distinct from the initial cotyledons (seed leaves), will appear and start the process of photosynthesis. This stage marks the seedling’s transition to a young plant capable of producing its own food through photosynthesis.
Seedling development is typically completed within seven to ten days of germination. Proper care during this phase ensures that the young plant grows robust and healthy, ready to continue its journey to maturity.
Troubleshooting Germination Issues
Non-Viable Seeds
- Identification: Seeds that don’t sprout may be old, damaged, or improperly stored. Non-viable seeds often remain dormant or rot.
- Solution: Use fresh, high-quality seeds from a reputable source. Avoid using seeds that appear damaged, discolored, or shrunken.
Inadequate Conditions
- Temperature: Ensure the environment is warm enough. Temperatures below 70°F (21°C) can slow or halt germination.
- Moisture: Maintain consistent moisture without waterlogging. Overly dry or waterlogged conditions can prevent germination.
- Light: While not essential for germination, some light may help stimulate growth. Once the seedling emerges, light becomes crucial for photosynthesis.
Incorrect Handling
- Damage: Avoid damaging the seed or the emerging radicle. Handle sprouted seeds with care during transplantation.
- Transplantation: Gently handle sprouted seeds when transplanting them to soil or other mediums. Rough handling can damage the delicate radicle and inhibit growth.

Tips for Successful Germination
- Use Fresh Seeds: Always start with fresh, high-quality seeds. New seeds have higher viability and germination rates than old ones do.
- Maintain Optimal Conditions: Keep the environment warm and moist. If necessary, use a heat mat to maintain consistent temperatures.
- Be Patient: Germination can take several days, so avoid the temptation to interfere. Check the seeds daily, but handle them as little as possible.
- Monitor Regularly: Check on the seeds daily to ensure they remain moist and at the right temperature. Adjust environmental conditions as needed.
- Gentle Handling: Be careful when transplanting sprouted seeds to avoid damaging the delicate radicle. Use tweezers or a similar tool for precise handling.
Conclusion
Germinating cannabis seeds is a critical step in the cultivation process. By understanding the factors that influence germination time and following best practices, you can ensure a successful start to your cannabis-growing journey. Whether you prefer the paper towel method, direct soil planting, or another technique, the key is to provide the right conditions and handle the seeds with care. With patience and attention, you’ll soon see your cannabis seeds sprout and begin their journey to becoming healthy, productive plants.
Now that you’ve learned how long it takes for cannabis seeds to sprout, shop the collection of regular, feminized, and autoflower cannabis seeds at Seeds Here Now.
Suggested Articles
;)
;)
;)




 04 Feb 2026
04 Feb 2026  7 min read
7 min read


 May 20, 2024
May 20, 2024 


RESPONSES (0)
No responses yet. Be the first to respond!