Indoor vs. Outdoor Growing: Pros and Cons
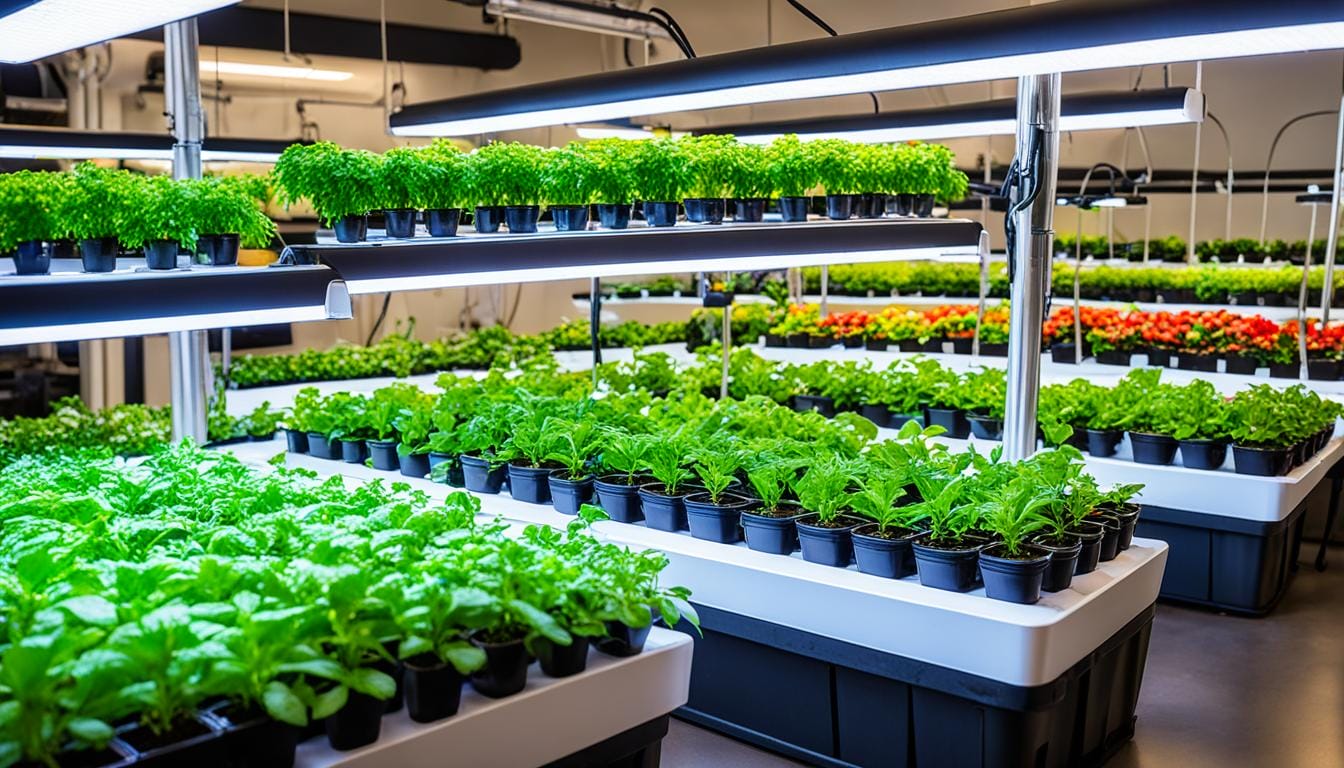

Did you know that indoor gardening is becoming increasingly popular in the United States? According to a recent study, the indoor gardening market is projected to reach a value of $7.61 billion by 2027, with a compound annual growth rate of 22.6%. This statistic highlights the growing interest in cultivating plants indoors, but what are the advantages and disadvantages of indoor and outdoor growing? In this article, we will explore the pros and cons of each method, helping you make an informed decision for your own gardening journey.
Key Takeaways:
- Indoor gardening is a rapidly growing market in the United States, projected to reach a value of $7.61 billion by 2027
- This article will compare the pros and cons of indoor and outdoor growing, helping you make an informed decision
Understanding Indoor and Outdoor Cultivation
When it comes to cultivating plants, there are key differences between indoor and outdoor methods that can significantly impact the success of your gardening endeavors. In this section, we will explore these differences and discuss the advantages and drawbacks of each approach. By understanding the nuances of indoor and outdoor cultivation, you’ll be better equipped to decide which method suits your needs and goals.
Indoor and outdoor cultivation methods each have their unique benefits and challenges. By weighing these factors, you can determine which approach is better for your specific growing requirements.
Indoor Cultivation
Indoor cultivation involves growing plants in a contained environment, such as a greenhouse, grow tent, or dedicated indoor space. Many growers choose indoor cultivation for its precise control over environmental conditions, which can lead to higher yields and faster growth rates. It also provides protection from external elements such as pests and extreme weather conditions.
One popular indoor cultivation technique is hydroponics, which involves growing plants in nutrient-rich water solutions without the use of soil. This method allows for efficient nutrient absorption and accelerated plant growth. Another technique, aeroponics, utilizes a misting system to deliver nutrients directly to plant roots, resulting in even greater efficiency and faster growth.
| Advantages of Indoor Cultivation | Drawbacks of Indoor Cultivation |
|---|---|
|
|
Outdoor Cultivation
Outdoor cultivation involves growing plants in natural sunlight and soil, harnessing the power of the outdoors to nurture healthy and vibrant crops. This method offers the advantage of larger growing spaces and lower operational costs compared to indoor cultivation. It also allows for a more natural, organic approach to gardening.
When cultivating outdoors, growers rely on the natural lighting provided by the sun. However, some may choose to supplement natural light with artificial outdoor lighting options like LED or HID grow lights to extend the daily photoperiod or provide additional light during cloudy periods.
| Advantages of Outdoor Cultivation | Drawbacks of Outdoor Cultivation |
|---|---|
|
|
Whether you choose indoor or outdoor cultivation, it’s crucial to weigh the advantages and drawbacks of each method based on your specific circumstances and goals. Consider factors such as available space, budget, desired yield, and level of control over environmental conditions.
Benefits of Indoor Growing
Indoor growing presents numerous benefits for cultivators, offering greater control over environmental conditions, protection from pests and diseases, and the opportunity to incorporate advanced hydroponic systems. Let’s explore these advantages in more detail.
1. Greater Control over Environmental Conditions
One of the key advantages of indoor growing is the ability to have precise control over the growing environment. By utilizing technologies such as grow lights, ventilation systems, and temperature and humidity controllers, growers can create optimal conditions for plant growth.
This level of control allows for year-round cultivation, irrespective of external factors such as weather or geographic location. Whether you live in a region with extreme climates or simply want to grow plants that are not well-suited to your local conditions, indoor growing provides a solution.
2. Protection from Pests and Diseases
Another significant benefit of indoor growing is the reduced risk of pests and diseases. When plants are grown outdoors, they are subjected to a multitude of potential threats from insects, rodents, birds, and plant pathogens.
Indoor cultivation mitigates these risks by providing a controlled environment that can be sealed off from external pests and pathogens. Additionally, rigorous sanitation practices and careful monitoring can help prevent the occurrence and spread of plant diseases.
3. Advanced Hydroponic Systems
Indoor growing opens up the possibility of implementing advanced hydroponic systems. Hydroponics is a soilless cultivation method that replaces traditional soil with nutrient-rich water solutions, allowing for direct delivery of essential nutrients to plant roots.
This approach offers numerous advantages over traditional soil-based growing, including faster growth rates, higher yields, and efficient water usage. Furthermore, hydroponics enables growers to maximize space utilization and reduce the need for extensive crop rotations.
Advantages of Outdoor Growing
When it comes to cultivating plants, outdoor growing offers a range of unique advantages that make it an appealing choice for many growers. In this section, we will explore the benefits of outdoor growing and the reasons why some enthusiasts prefer this method.
Natural Sunlight
One of the most significant advantages of outdoor growing is access to natural sunlight. Sunlight provides plants with a full spectrum of light that promotes healthy growth and maximizes their potential. Unlike indoor lighting systems, natural sunlight is free and does not require additional energy or maintenance costs.
Lower Costs
Outdoor growing can be more cost-effective compared to indoor cultivation. With outdoor growing, you eliminate much of the need for expensive growing equipment and lights, thereby reducing energy consumption and utility bills. Additionally, you can take advantage of natural precipitation, reducing the need for artificial irrigation systems.
Ability to Grow on a Larger Scale
Outdoor growing allows you to take advantage of larger spaces, enabling you to grow plants on a larger scale. This is particularly beneficial for commercial growers or individuals looking to maximize their yield. With ample space and natural airflow, plants have more room to thrive and spread their roots, resulting in healthier and more abundant crops.
“Outdoor growing provides the perfect environment for plants to harness the power of nature. The combination of natural light, fresh air, and ample space creates optimal conditions for robust growth and bountiful harvests.”
While outdoor growing comes with its advantages, it’s important to consider factors such as climate, weather changes, and regional regulations that can impact the success of your outdoor garden.
| Advantages of Outdoor Growing | Indoor Growing |
|---|---|
| Natural sunlight for optimal plant growth | Reliance on artificial lighting systems |
| Lower costs (no need for additional lighting and reduced energy consumption) | Higher energy consumption and utility bills |
| Ability to grow on a larger scale | Limited space and capacity |
By harnessing the power of natural sunlight, reducing costs, and having the ability to grow on a larger scale, outdoor growing presents exciting opportunities for plant enthusiasts. Whether you choose outdoor or indoor cultivation ultimately depends on your specific circumstances, resources, and preferences.
Comparing Yields: Indoor vs. Outdoor
When it comes to deciding between indoor and outdoor growing, one crucial factor to consider is yield. The amount of produce you can harvest from your cultivation method can significantly impact your overall success and satisfaction as a grower. In this section, we will analyze the potential yield differences between indoor and outdoor growing, considering various factors that influence productivity.
Factors Affecting Yield
Several factors contribute to the yield differences between indoor and outdoor cultivation. Let’s take a closer look at some key considerations:
- Lights and lighting efficiency: Indoor growers rely on artificial lighting sources, such as LEDs, HID, or fluorescent lights, to provide the necessary light spectrum for plant growth. The quality and efficiency of these lights can greatly impact yields.
- Environmental control: Indoor growers have greater control over environmental conditions, including temperature, humidity, airflow, and CO2 levels. Maintaining optimal conditions can promote healthier and more vigorous growth, leading to higher yields.
- Genetics and strain selection: The choice of plant genetics and strains can influence yield potential. Some strains are better suited for indoor environments, while others thrive in outdoor settings.
- Pest and disease management: Indoor growers benefit from reduced exposure to pests and diseases, thanks to the controlled environment. Preventing or managing these threats effectively can help safeguard yield.
- Cultivation technique: The choice of cultivation technique can also impact yield. Indoor growers commonly use methods like hydroponics or aeroponics, which offer efficient nutrient delivery and optimal root oxygenation.
While indoor cultivation provides more control over the growing environment, outdoor growing has its advantages as well.
Growing cannabis outdoors allows the plants to benefit from natural sunlight, which provides the full spectrum of light needed for optimal growth. Additionally, outdoor growing can save on energy costs associated with artificial lighting.
However, outdoor growing is subject to factors beyond control, such as weather changes and regional regulations, which can affect yields.
Comparative Yield Data
To illustrate the potential yield differences between indoor and outdoor cultivation, let’s examine hypothetical data:
| Yield Metric | Indoor | Outdoor |
|---|---|---|
| Harvestable Plant Count | 60 | 100 |
| Average Yield per Plant (grams) | 200 | 100 |
| Total Yield (grams) | 12,000 | 10,000 |
The table above represents a simplified comparison of yield metrics based on hypothetical data. While the outdoor cultivation method has a higher plant count, the indoor method results in a higher average yield per plant. Consequently, the total yield slightly favors indoor cultivation in this example.
It’s important to note that actual yield outcomes may vary depending on various factors, including grower experience, strain selection, cultivation techniques employed, and the level of expertise in managing plant growth.
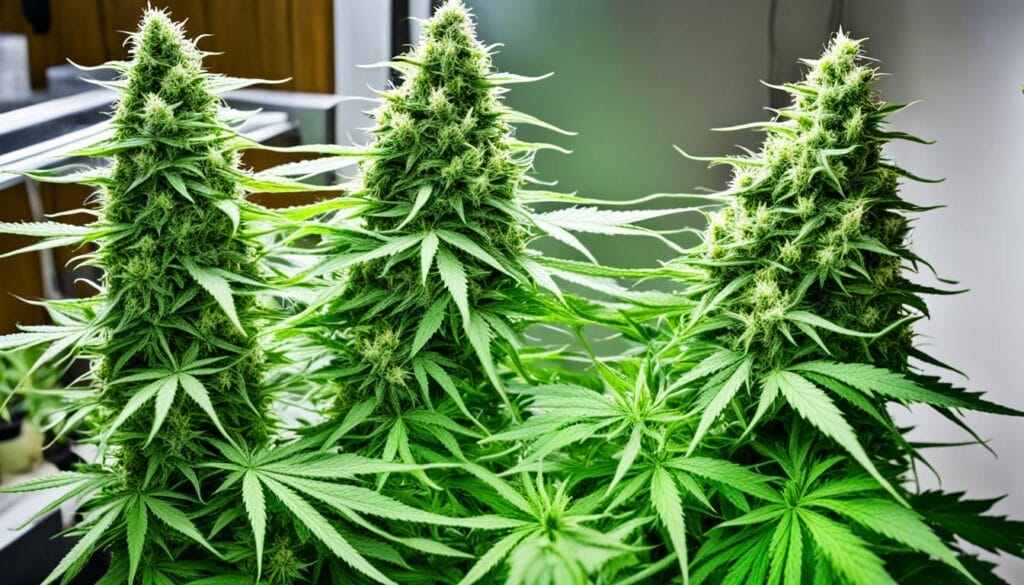

To optimize your yield potential, it’s crucial to select the cultivation method that aligns with your goals, available resources, and growing conditions. The decision between indoor and outdoor growing ultimately depends on your specific circumstances and preferences.
Choosing the Right Method for You
When it comes to cultivation, there are two primary options: indoor and outdoor growing. Deciding which method is best for you requires careful consideration of several factors. Let’s explore how you can make an informed decision between indoor and outdoor growing.
Location
Your geographical location plays a significant role in determining whether indoor or outdoor growing is more suitable for you. Consider the climate and weather conditions in your area. If you live in a region with harsh winters or extreme temperatures, indoor cultivation provides a controlled environment that protects your plants from unfavorable conditions.
Available Resources
Assess the resources you have at your disposal. Indoor growing often requires more investment in equipment such as grow lights, ventilation systems, and hydroponic setups. On the other hand, outdoor growing relies on natural sunlight and requires less initial investment. Evaluate your budget and determine which option aligns better with your financial resources.
Desired Output
Consider your goals and the quantity of plants you intend to grow. If you’re looking for a small-scale operation or primarily cultivating for personal use, indoor growing might be a suitable choice. Indoor cultivation allows for better control over plant growth and can deliver consistent yields. However, if you plan to grow on a larger scale and produce higher volumes, outdoor growing provides more space and resources to accommodate your needs.
Personal Preferences
Your personal preferences and gardening style are crucial factors to consider. Some individuals enjoy the hands-on approach of tending to plants indoors, while others find satisfaction in working with nature and the outdoors. Reflect on what brings you joy and fulfillment as a grower, and let that guide your decision.
By weighing these factors—location, available resources, desired output, and personal preferences—you can make an informed choice between indoor and outdoor growing. It’s essential to find a method that aligns with your circumstances and allows you to cultivate plants successfully.
Remember, it’s not a matter of which method is better overall, but which one is better for you and your specific needs. Now that you have a better understanding of the factors to consider, you’re one step closer to embarking on an exciting cultivation journey.
| Factors | Indoor Growing | Outdoor Growing |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Can be done anywhere, regardless of climate | Dependent on regional weather conditions |
| Control | Complete control over environmental conditions | Relies on natural elements |
| Cost | Higher initial investment for equipment | Lower overhead costs |
| Yield | Potential for consistent, controlled yields | Potential for larger, outdoor yields |
| Space | Can be done in limited spaces | Requires more land for expansion |
Indoor Growing Techniques
When it comes to indoor growing, there are various techniques that growers can employ to cultivate their plants. In this section, we will explore three commonly used methods: traditional soil-based growing, hydroponics, and aeroponics. Each technique has its own advantages and considerations, allowing growers to choose the approach that best suits their needs and preferences.
1. Traditional Soil-Based Growing
Traditional soil-based growing is the most familiar and widely practiced technique. It involves using soil as the growing medium to provide plants with essential nutrients. Many growers appreciate this method for its simplicity and the familiarity of working with soil. Moreover, soil acts as a natural buffer, helping to maintain stable moisture levels and offering good support for plant growth.
Soil-based growing provides a sense of connection to the natural world. It allows you to work with the Earth’s elements and creates a nurturing environment for your plants.
However, it is important to note that soil-based growing requires regular monitoring and maintenance to ensure proper nutrient balance and prevent issues such as overwatering or nutrient deficiencies. Additionally, it can be challenging to precisely control the pH level of the soil, which may impact plant health and yield.
2. Hydroponics
Hydroponics is a soilless growing technique that involves growing plants in a nutrient-rich water solution. The plants’ roots are supported by an inert medium, such as coconut coir or perlite, while a water pump or aerator supplies the roots with the necessary oxygen. This method offers several benefits, including:
- Improved water and nutrient efficiency
- Faster growth rates and increased yields
- Greater control over nutrient uptake
- Reduced risk of pests and diseases
Hydroponics also allows for precise control over pH and nutrient levels, ensuring optimal plant growth. However, setting up a hydroponic system can be more complex and costly compared to traditional soil-based growing. Ongoing maintenance is required to monitor water quality, nutrient levels, and the functionality of the system components.
3. Aeroponics
Aeroponics is an advanced soilless growing technique that suspends plant roots in mid-air and mists them with a nutrient-rich solution. The roots receive oxygen through periodic misting cycles, promoting rapid growth and efficient nutrient absorption. Some key benefits of aeroponics include:
- Faster growth rates and higher yields
- Reduced water and nutrient consumption
- Minimal use of growing space
- Lower risk of pests and diseases
Aeroponics is especially suitable for plants with delicate root systems, such as leafy greens and herbs. However, it requires precise control over environmental conditions and regular monitoring to ensure the misting cycles are functioning correctly. The initial setup costs for an aeroponic system can be higher compared to other indoor growing techniques.
| Technique | Advantages | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Soil-Based Growing | – Familiarity and connection to nature – Stable moisture levels and support for plant growth |
– Regular monitoring and maintenance – Challenging pH control |
| Hydroponics | – Improved water and nutrient efficiency – Faster growth rates and increased yields – Precise control over nutrient uptake |
– Higher setup and maintenance costs – Complex setup and monitoring |
| Aeroponics | – Faster growth rates and higher yields – Reduced water and nutrient consumption – Minimal use of growing space |
– Precise environmental control – Higher initial setup costs |
By understanding the benefits and considerations of each indoor growing technique, you can choose the method that aligns with your goals and resources. Whether you prefer the simplicity of traditional soil-based growing, the efficiency of hydroponics, or the innovation of aeroponics, indoor cultivation provides numerous advantages for cultivating healthy and thriving plants.
Outdoor Growing Considerations
When it comes to cultivating plants, deciding whether to grow indoors or outdoors is a crucial choice. While indoor growing offers control and convenience, outdoor growing has its own perks. In this section, we will focus on the considerations and factors to keep in mind for successful outdoor cultivation.
Climate
The first and most important consideration for outdoor growing is the climate of your region. Different plants thrive in different climates, so it’s essential to choose varieties that are well-suited to your specific environment. Some plants require specific temperature ranges or specific seasons to grow, while others are more adaptable.
Soil Quality
The quality of your soil plays a significant role in the success of your outdoor garden. It’s important to assess the soil conditions, such as its pH level and nutrient content, before planting. Conducting a soil test can provide valuable insights and help you make informed decisions about fertilizers and amendments to optimize plant growth.
Pest Control
Outdoor gardens are more susceptible to pests, including insects and wildlife. Implementing effective pest control strategies is essential to protect your plants from potential damage. Organic pest control methods, such as companion planting and natural repellents, can help minimize the impact of pests without relying on harmful chemicals.
Protection from Extreme Weather
Outdoor gardens are exposed to the elements, making them vulnerable to extreme weather conditions such as strong winds, heavy rain, or hailstorms. Implementing protective measures, such as installing windbreaks or using row covers, can help shield your plants from these natural forces and increase their chances of thriving.
Proper Plant Spacing
When growing outdoors, it’s crucial to give your plants adequate space to grow and receive proper airflow. Crowded plants can lead to increased humidity and create an environment favorable to the development of diseases. Be sure to follow the recommended spacing guidelines for the specific plant varieties you are growing.
Managed Irrigation
Unlike indoor cultivation, outdoor gardens rely on natural rainfall for irrigation. However, depending on your region’s climate and precipitation patterns, supplementing with additional watering may be necessary. Monitoring soil moisture levels and practicing proper irrigation techniques will help ensure your plants receive the right amount of water without becoming oversaturated.
Consideration Summary
When opting for outdoor growing, it’s important to consider factors such as climate, soil quality, pest control, weather protection, plant spacing, and irrigation. By taking these considerations into account and planning accordingly, you can create an environment that promotes healthy plant growth and maximizes your outdoor cultivation success.
Next, we will explore the different lighting options available for indoor growing in Section 9, helping you optimize conditions for plants growing in controlled environments.
| Indoor Growing | Outdoor Growing |
|---|---|
|
|
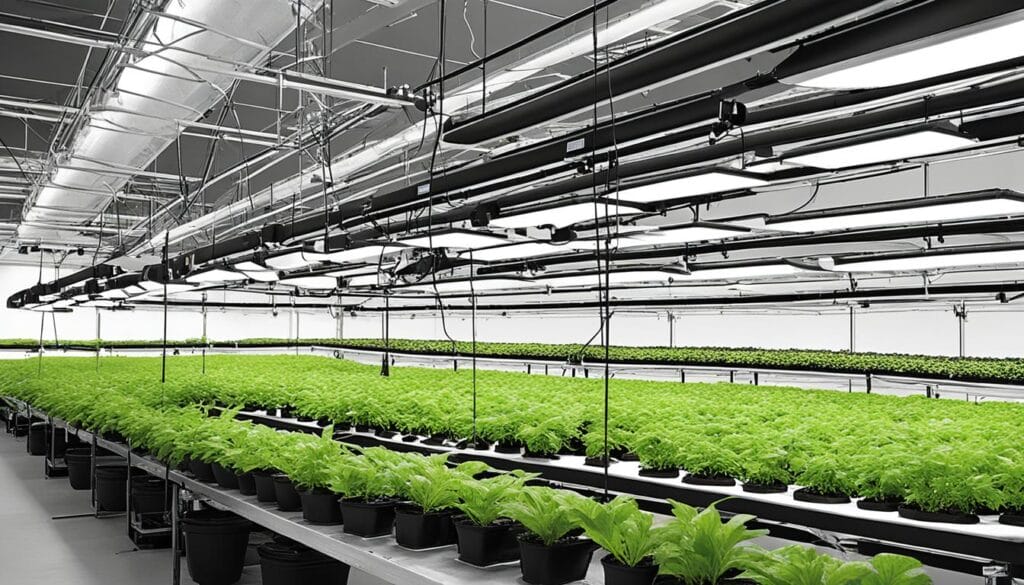

Lighting Options for Indoor Growing
Proper lighting plays a crucial role in the success of indoor growing. When it comes to creating the optimal light conditions for your indoor garden, you have several options to consider. In this section, we will explore the different lighting options available to indoor cultivators and compare them to outdoor lighting.
LED Lights
Light-emitting diode (LED) lights are a popular choice for indoor growers due to their energy efficiency and versatility. These lights emit low heat, reducing the risk of damaging delicate plants. LED lights also provide a full spectrum of light, which can be tailored to the specific needs of different plant growth stages. They are known for their long lifespan and low maintenance requirements, making them a cost-effective choice in the long run.
HID Lights
High-intensity discharge (HID) lights are another common lighting option for indoor gardens. They include metal halide (MH) and high-pressure sodium (HPS) lights. MH lights produce a cooler, blueish light spectrum that is ideal for the vegetative stage of plant growth, promoting leafy growth. HPS lights emit a warmer, reddish light spectrum that is suitable for the flowering and fruiting stages. HID lights are known for their high light intensity, which allows for greater penetration and coverage, resulting in robust plant growth and higher yields.
Fluorescent Lights
Fluorescent lights are a cost-effective choice for small-scale indoor gardens and for starting seedlings. They are energy-efficient and produce less heat than HID lights, making them suitable for plants with low light requirements or those that prefer cooler temperatures. While not as powerful as LED or HID lights, fluorescent lights provide a balanced spectrum of light that supports healthy plant growth in various stages.
In comparison to outdoor lighting, indoor lighting systems offer the advantage of providing consistent and controllable light conditions for your plants. This ensures that your plants receive the necessary amount and quality of light regardless of the external factors. However, it is important to consider the initial investment and energy consumption associated with indoor lighting systems.
Now that we have explored the different lighting options available for indoor growing, it’s time to delve into the control and optimization of the environmental conditions in indoor cultivation. In the next section, we will discuss the importance of maintaining the right temperature, humidity, airflow, and CO2 levels for optimal indoor growing results.
Environmental Control in Indoor Growing
Maintaining optimal environmental conditions is crucial for successful indoor growing. By carefully managing temperature, humidity, airflow, and CO2 levels, growers can create an ideal environment that maximizes plant growth and productivity.
The Importance of Temperature
Temperature plays a vital role in indoor cultivation. Different plants have specific temperature requirements for optimal growth. Too hot or too cold temperatures can negatively impact plant health and development.
For most plants, the ideal temperature range is between 70 degrees Fahrenheit (21°C) and 80 degrees Fahrenheit (27°C) during the day, and slightly cooler at night. However, it’s important to research the specific temperature preferences of the plants you are growing to ensure they thrive.
Controlling Humidity
Humidity levels also significantly affect indoor growing. High humidity can increase the risk of mold and fungal diseases, while low humidity can lead to plant dehydration and stunted growth.
Aim for a relative humidity (RH) level between 50 percent and 60 percent during the vegetative stage and slightly lower, around 40 percent to 50 percent, during the flowering stage. Using a hygrometer or humidity controller can help monitor and maintain optimal humidity levels.
Managing Airflow
Air circulation is essential for indoor growing as it helps prevent stagnant air conditions, control temperature, and ensure proper CO2 distribution.
Investing in an oscillating fan or multiple fans strategically placed around the grow space can promote healthy airflow. It’s crucial to ensure that there are no stagnant areas where hot or humid air can accumulate.
Adjusting CO2 Levels
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a vital element for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light into energy. Optimizing CO2 levels can significantly enhance plant growth and yield.
During the vegetative stage, maintain CO2 levels between 800 and 1200 parts per million (ppm). As the plants enter the flowering stage, reduce CO2 supplementation to around 600 to 800 ppm.
In any indoor growing setup, it’s essential to have proper ventilation systems and equipment to regulate temperature, humidity, airflow, and CO2 levels for optimal plant health and growth.
Environmental Control Parameters for Indoor Growing
| Parameter | Ideal Range | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 70°F – 80°F (21°C – 27°C) | Temperature affects growth rate and overall plant health. |
| Humidity | 50% – 60% RH (vegetative stage) 40% – 50% RH (flowering stage) |
Proper humidity levels prevent diseases and maintain optimal plant hydration. |
| Airflow | Continuous, gentle movement | Adequate airflow prevents stagnant conditions and ensures CO2 distribution. |
| CO2 Levels | 800 – 1200 ppm (vegetative stage) 600 – 800 ppm (flowering stage) |
Optimal CO2 levels support enhanced photosynthesis and growth. |
Factors Impacting Outdoor Cultivation
When deciding between indoor and outdoor cultivation, it’s essential to consider the various factors that can impact the success of your outdoor garden. Understanding the differences between indoor and outdoor growing methods and how these factors come into play can help you make an informed decision that aligns with your goals and resources.
Climate
The climate in your region plays a crucial role in outdoor cultivation. Different plants thrive in different climates, so it’s essential to select varieties that are well-suited to the temperatures, humidity levels, and rainfall patterns in your area. Some plants prefer cooler climates with moderate temperatures, while others thrive in hot, dry conditions.
Furthermore, changes in weather patterns throughout the year can also impact outdoor cultivation. Variations in temperature, rainfall, and sunshine can affect plant growth and development, making it necessary to adjust your cultivation methods accordingly. For example, you may need to provide additional shade during scorching summer months or protect your crops from frost in colder seasons.
Regional Regulations
Another factor to consider when opting for outdoor cultivation is the presence of regional regulations. Depending on your location, there may be specific restrictions or requirements governing outdoor growing. These regulations can pertain to the types of plants allowed, cultivation methods, and even plant height limitations.
It’s crucial to familiarize yourself with the local regulations before starting your outdoor garden to ensure compliance and avoid any legal issues. Research the applicable laws, permits, and any restrictions related to outdoor cultivation in your area.
Pests and Diseases
Outdoor cultivation puts your plants at a higher risk of encountering pests and diseases compared to indoor growing. In an open environment, plants are susceptible to pests such as insects, birds, and rodents, as well as diseases caused by fungi, bacteria, or viruses.
To manage these risks, it’s important to implement appropriate pest control measures and maintain good plant health. This may involve using organic pest repellents, setting up physical barriers, practicing crop rotation, and regularly inspecting your plants for any signs of infestation or disease.
Conclusion
Both indoor and outdoor growing methods offer unique advantages and challenges for cultivators. The decision of which method to choose ultimately depends on your specific circumstances and preferences. By carefully considering the information provided throughout this article, you can make an informed choice that aligns with your needs and goals for achieving optimal yields.
Indoor growing provides the advantage of greater control over environmental conditions, allowing growers to fine-tune factors such as temperature, humidity, and airflow. This level of control enables the implementation of advanced techniques like hydroponics and aeroponics, which can result in higher productivity and faster growth rates.
On the other hand, outdoor growing allows cultivators to harness the power of natural sunlight, reducing the need for artificial lighting and potentially lowering costs. It also offers the opportunity to grow on a larger scale, making it suitable for those with ample outdoor space and the desire to cultivate crops in a more natural, open environment.
Ultimately, the decision between indoor and outdoor growing depends on your location, available resources, desired output, and personal preferences. Whether you choose the precision and control of indoor cultivation or the reliance on nature in outdoor cultivation, make sure to assess your unique circumstances and make an informed decision that suits your needs. Happy growing!
Know that you understand the pros and cons of indoor vs outdoor cultivation, shop the collection of regular, feminized, and autoflower cannabis seeds at Seeds Here Now.
FAQ
What are the differences between indoor and outdoor cultivation?
Indoor cultivation involves growing cannabis plants in a controlled environment, such as a grow tent or greenhouse, while outdoor cultivation takes place in an open outdoor setting. The main differences between these methods include environmental control, lighting options, and potential yield.
Which is better, indoor or outdoor growing?
The choice between indoor and outdoor growing depends on your specific needs and preferences. Indoor growing offers greater control over environmental conditions and protection from pests, while outdoor growing provides natural sunlight and the ability to grow on a larger scale.
What are the benefits of indoor growing?
Indoor growing offers several advantages, such as greater control over environmental conditions, protection from pests and diseases, and the ability to implement advanced hydroponic systems. It also allows for year-round cultivation and the use of different growing techniques.
What are the advantages of outdoor growing?
Outdoor growing has its unique benefits, including access to natural sunlight, lower costs, and the ability to grow on a larger scale. It also allows for more diverse strains and can provide a more natural growing environment in certain regions.
How do indoor and outdoor yields compare?
Indoor cultivation typically yields higher-quality buds and allows for more control over the growth process. However, outdoor cultivation can result in larger overall yields due to the natural sunlight and the ability to cultivate larger plants.
How can I choose the right method for me?
When choosing between indoor and outdoor growing, consider factors such as your location, available resources, desired output, and personal preferences. Assess the advantages and challenges of each method and determine which aligns best with your goals and circumstances.
What are some popular indoor growing techniques?
Indoor growers commonly use traditional soil-based methods, hydroponics, and aeroponics. Each technique has its own advantages and considerations, such as nutrient control, water usage, and ease of maintenance.
What considerations should I keep in mind for outdoor growing?
Successful outdoor cultivation requires careful planning and consideration of factors such as climate, soil quality, and pest control. You may need to adapt your growing techniques based on your specific outdoor environment.
What lighting options are available for indoor growing?
Indoor growers have several lighting options to choose from, including LED, HID, and fluorescent lights. Each lighting option has its own pros and cons, such as energy efficiency, spectrum control, and initial cost.
How can I control the environment in indoor growing?
Indoor growers can manipulate factors such as temperature, humidity, airflow, and CO2 levels to create an optimal growing environment. This level of control allows for precise adjustments and can result in higher-quality yields.
What factors can impact outdoor cultivation?
Outdoor cultivation is influenced by factors such as climate, weather changes, and regional regulations. Understanding your local climate and adapting your growing practices accordingly is crucial for successful outdoor cultivation.
Suggested Articles
;)
;)
;)




 10 Feb 2026
10 Feb 2026  7 min read
7 min read


 February 21, 2024
February 21, 2024 


RESPONSES (0)
No responses yet. Be the first to respond!