Cannabis Plant Life Cycle Stages Explained
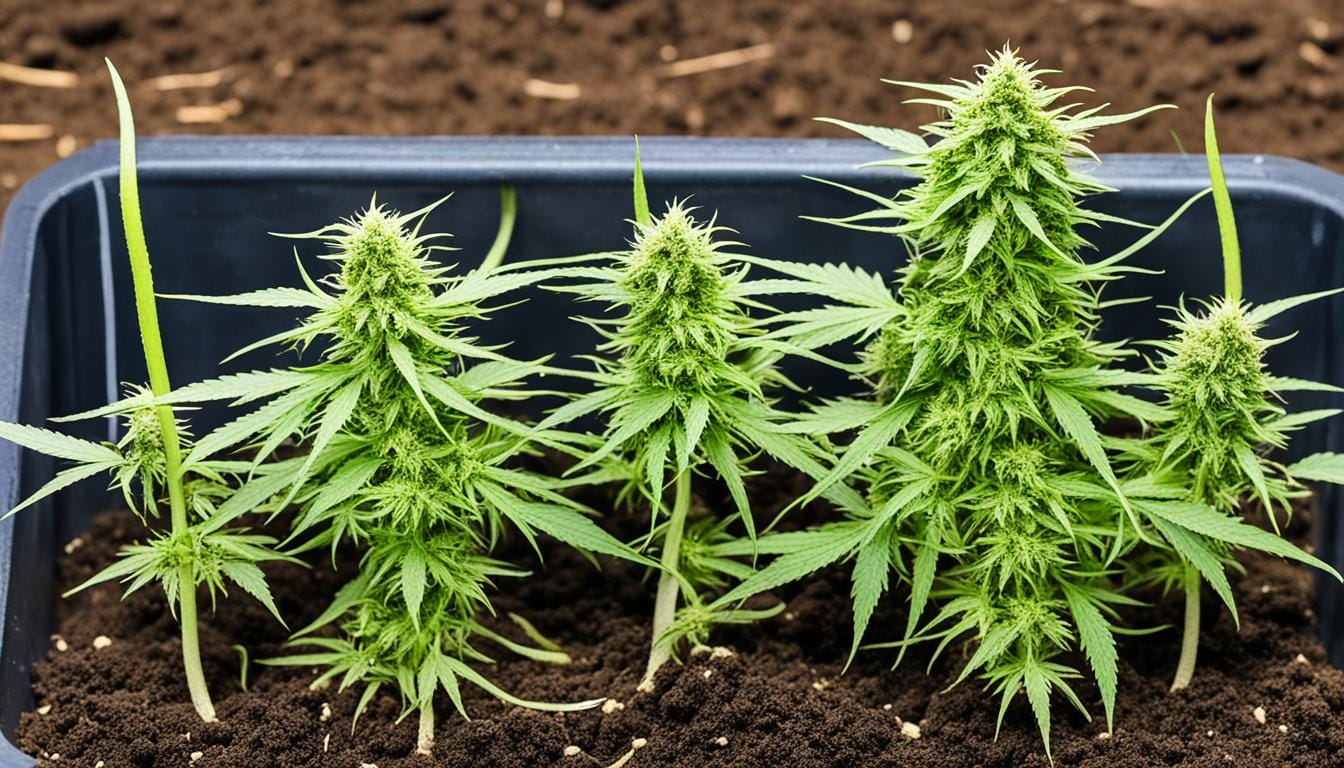

Did you know that the cannabis plant goes through several distinct stages in its life cycle, each one crucial for its growth and development? From germination to harvest, understanding these cannabis growth stages is essential for successful cultivation and maximizing yield.
In this article, we will guide you through the fascinating journey of a cannabis plant, explaining the marijuana plant development process and the key characteristics of each stage. Whether you’re a novice cultivator or an experienced grower, this comprehensive guide will provide valuable insights into the cannabis plant flowering stages and other important milestones in the weed plant growth phases.
Key Takeaways:
- Understanding the cannabis plant life cycle is crucial for successful cultivation.
- The stages include germination, seedling, vegetative growth, flowering, and harvest.
- Each stage requires specific care, including proper light, nutrients, and environmental conditions.
- Knowing when to harvest and how to trim the plants is essential for preserving quality.
- Advanced techniques and plant health strategies can further optimize your cultivation process.
Understanding Germination
Germination is the first and crucial stage in the cannabis plant life cycle. It sets the foundation for healthy growth and abundant harvests. In this section, we will delve into the process of germination, explaining its significance and providing valuable insights into ensuring successful germination.
Germination begins with the quality of the seeds. It’s essential to source high-quality cannabis seeds from reputable suppliers like SeedsHereNow.com. Quality seeds have a higher chance of germinating and developing into strong, vigorous plants.
The soil conditions play a vital role in the germination process. The soil should be loose, well-draining, and rich in organic matter. This provides the ideal environment for the seeds to absorb water and nutrients, kickstarting their growth.
Proper technique is also crucial for successful germination. Whether you choose the paper towel method, the direct-to-soil method, or germination cubes, ensuring the right level of moisture and temperature is essential. Maintaining a warm and humid environment stimulates the seeds to sprout.
“Germination is a delicate yet exciting phase of the cannabis plant life cycle. It’s the beginning of a journey that leads to the development of beautiful plants with potent buds.”
Recommendations for Successful Germination
- Use high-quality cannabis seeds from a reliable supplier.
- Prepare a well-draining soil rich in organic matter.
- Apply a suitable germination technique based on your preference and growing setup.
- Maintain a consistent temperature and humidity level for optimal seed development.
- Monitor closely and provide gentle care during this delicate stage.
Understanding the germination stage is imperative for every cannabis cultivator. It sets the tone for the rest of the plant’s development. By following the recommended practices and paying attention to the needs of your seeds, you can ensure a successful germination process and enjoy the rewards of healthy and robust cannabis plants.
The Seedling Stage
As we continue our journey through the cannabis plant’s life cycle, we now enter the seedling stage. This is a crucial phase where the young cannabis plants begin to establish their roots and develop their initial set of leaves.
During the seedling stage, it’s important to provide the optimal environmental conditions that promote healthy growth. Here are some key characteristics of seedlings and essential care practices to consider:
- Environmental requirements:
To ensure successful seedling development, maintain a temperature range of 70-80°F (21-27°C) and a humidity level of 50-70%. This will create a favorable environment for root development and overall plant growth. - Light exposure:
Seedlings require gentle and consistent light exposure to avoid stretching or stunting. Provide 18-24 hours of light per day using fluorescent or LED lights positioned 2-4 inches above the plants. This will encourage healthy leaf development and prevent the plants from becoming leggy. - Watering routine:
Seedlings have delicate root systems that require careful watering. Avoid overwatering, as it can lead to damping-off or root rot. Instead, water the seedlings when the top inch of the soil feels dry, using a gentle stream of water to prevent damage to the fragile plants. - Nutrient supplementation:
During the seedling stage, cannabis plants rely on the nutrients stored in the seed. Therefore, it is unnecessary to provide additional nutrients at this early stage. In fact, overfeeding can harm the delicate seedlings. Wait until the plants develop a stronger root system before introducing nutrients.
By understanding the needs of seedlings and providing them with the right conditions, you can ensure healthy growth and set the stage for a successful cannabis cultivation journey.
“The seedling stage is like watching a tiny miracle unfold. Taking care of these fragile plants during this phase sets the foundation for a bountiful harvest.” – Jane Doe, Experienced Cultivator
Vegetative Growth
During the vegetative growth stage, providing your cannabis plants with the optimal light, nutrients, and environmental conditions is crucial for their healthy development. This stage is characterized by rapid growth as the plant focuses on foliage expansion and root system establishment.
Lighting plays a key role in promoting vegetative growth. Cannabis plants require a minimum of 18 hours of light per day, mimicking the long days of summer. High-intensity grow lights, such as metal halide (MH) or high-pressure sodium (HPS) lights, are commonly used to provide the necessary light intensity for vigorous growth.
In terms of nutrients, nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) are essential for healthy vegetative growth. A balanced fertilizer with elevated levels of nitrogen promotes leafy growth and vibrant green foliage. Supplementing with micronutrients like calcium, magnesium, and iron ensures optimal plant health.
Environmental factors, such as temperature and humidity, also play a vital role in vegetative growth. Maintaining a temperature range of 70-85°F (21-29°C) and a humidity level around 50-70% creates an ideal environment for robust growth. Adequate air circulation and ventilation prevent the build-up of excess moisture, preventing the risk of mold and pests.
Pruning and training techniques can further enhance plant structure and increase yield potential during the vegetative growth stage. Topping, which involves cutting off the top growth tip, encourages bushier growth and the development of multiple colas. LST (Low-Stress Training) techniques, such as tying down or bending branches, promote an even canopy and allow for better light penetration.
By understanding and implementing the right practices during the vegetative growth stage, you can ensure your cannabis plants develop into healthy, robust specimens ready to transition into the flowering stage.
Key Considerations for Vegetative Growth:
- Provide a minimum of 18 hours of light per day
- Choose high-intensity grow lights like metal halide (MH) or high-pressure sodium (HPS)
- Use a balanced fertilizer with elevated nitrogen levels
- Supplement with micronutrients for optimal plant health
- Maintain a temperature range of 70-85°F (21-29°C) and a humidity level around 50-70%
- Ensure proper air circulation and ventilation
- Implement pruning and training techniques like topping and LST
Now that we have covered the essentials of vegetative growth, let’s move on to the next stage: the transition to flowering.
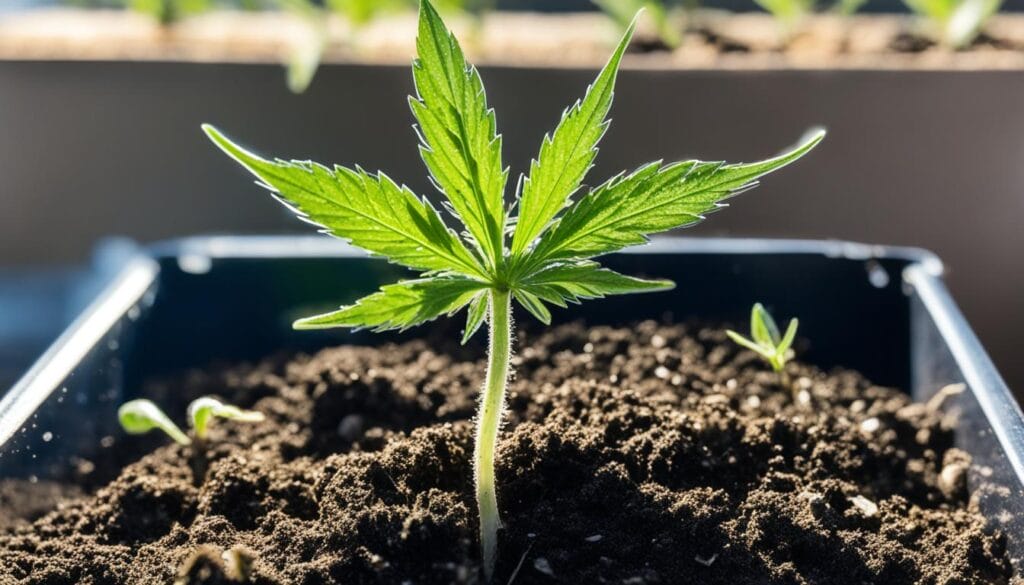

Transition To Flowering
As the cannabis plant progresses from the vegetative growth stage to the flowering stage, a significant transformation takes place. This transition is triggered by specific environmental cues and hormonal changes within the plant. Understanding the nuances of this phase is crucial for cultivators aiming to achieve a successful and abundant yield.
The transition to flowering is an exciting and pivotal stage in the cannabis plant’s life cycle. It marks the beginning of the reproductive phase, where the plant shifts its energy from growth and development to producing flowers.
One of the key triggers for this transition is the change in light cycles. Cannabis plants typically require a specific balance of light exposure to induce flowering. The most common light cycle for this stage is 12 hours of light, followed by 12 hours of uninterrupted darkness. This light schedule mimics the natural photoperiod conditions found during the fall season, signaling to the plant that it’s time to flower.
Additionally, nutrient requirements alter during the flowering stage. Cannabis plants demand higher levels of phosphorus and potassium to support flower development. Nitrogen levels, on the other hand, should be reduced to prevent excessive vegetative growth and promote floral growth.
The flowering stage of the cannabis plant is characterized by the emergence of vibrant and aromatic flowers, also known as buds. These buds contain the coveted cannabinoids and terpenes that give each strain its unique qualities and effects. It’s important to provide the right environmental conditions, including appropriate temperature, humidity, and air circulation, to ensure optimal bud development and prevent mold or pest infestations.
Pistils, Trichomes, and Harvest Timing
During the flowering stage, the plant’s reproductive structures, such as pistils and trichomes, play a crucial role in determining the maturity and readiness for harvest. Pistils are hair-like structures that protrude from the flower’s calyxes, and their color changes throughout the flowering stage. Initially, pistils are white and slowly transition to a vibrant orange or red hue as the plant nears maturity.
Trichomes, on the other hand, are the resinous glands that cover the buds and leaves. They contain the cannabinoids and terpenes that give cannabis its therapeutic and recreational properties. Trichomes go through different stages of development, from clear to cloudy and finally to a hint of amber, and the ideal harvest timing can be determined by closely observing these changes.
| Stage of Trichomes | Harvest Timing |
|---|---|
| Clear (transparent) | Early harvest for a more cerebral effect |
| Cloudy (milky) | Peak potency and desired effects |
| Amber (slightly yellow) | Harvest for a more sedative and relaxing effect |
It’s essential to consider personal preferences and the desired effects when choosing the optimal harvest timing based on trichome appearance. Some cultivators prefer harvesting when trichomes are mostly cloudy, while others may wait for a higher percentage of amber trichomes for a more relaxing experience.
Understanding the transition from vegetative growth to flowering is key to manipulating the cannabis plant’s natural lifecycle and optimizing yields. With the right light cycles, nutrient adjustments, and careful observation of pistils and trichomes, cultivators can foster the production of high-quality, cannabinoid-rich flowers.
Flowering Stage
During the flowering stage of the cannabis plant life cycle, significant physical changes occur. This phase is characterized by the development of buds, pistils, and trichomes, marking the onset of reproductive maturity. Understanding the nuances of the flowering stage is crucial for optimizing flower quality and yield.
Development of Buds
Buds are the prized flowers of the cannabis plant, containing high concentrations of cannabinoids and terpenes. As the flowering stage progresses, buds begin to form at the nodes of the plant. These compact clusters of densely packed calyxes are the primary source of cannabinoids, including THC and CBD.
To support healthy bud development, cultivators must ensure that plants receive adequate nutrients, particularly phosphorus and potassium. Proper nutrition and the right balance of macronutrients are crucial for the production of large, dense, and resinous buds.
Emergence of Pistils
Pistils, also known as stigmas, are hair-like structures that protrude from the buds. They play a critical role in the pollination process, capturing pollen for fertilization. However, in a controlled indoor cultivation environment, pistils serve as indicators of the plant’s sex and overall maturity.
During the early flowering stage, pistils emerge as tiny, white or pale-colored hairs. As the plant matures, these pistils change color, transitioning to vibrant red, orange, or brown. Observing the color change of pistils can help determine the ideal time for harvest.
Trichome Production
Trichomes are the resin glands that cover the surfaces of buds, leaves, and stems. These glistening structures are the epicenter of cannabinoid production and contain the highest concentrations of THC and CBD. Trichomes not only contribute to the potency of the flower but also provide essential flavors and aromas.
As the flowering stage progresses, trichomes undergo various transformations. Initially, they appear as small, translucent droplets. Over time, they develop into cloudy or milky white structures. For those seeking maximum psychoactive effects, harvesting at this stage is ideal. However, some cultivators prefer to wait until trichomes turn amber or brown for a more relaxing, sedative effect.
Monitoring trichome development and color is essential for achieving desired effects and flavors. Trichome observation requires magnification tools such as a jeweler’s loupe or a digital microscope.
Optimizing Flower Quality and Yield:
- Provide the appropriate light spectrum during the flowering stage. Cannabis plants require a different light cycle in the flowering stage compared to the vegetative stage. Most growers switch to a 12/12 light cycle (12 hours of light and 12 hours of uninterrupted darkness).
- Maintain proper humidity levels. High humidity can lead to issues such as mold and bud rot, while low humidity can cause plants to become stressed and reduce resin production.
- Monitor and adjust nutrient levels. The nutritional needs of cannabis plants change during different growth stages. Providing the right balance of nutrients, including phosphorus and potassium, is crucial for healthy bud development.
- Consider training techniques. Techniques such as topping, defoliation, and lollipopping can help promote even canopy development, light penetration, and bigger buds.
Harvest and Trimming
Once your cannabis plants have gone through the various growth stages, it’s time to reap the rewards of your hard work. In this section, we will explore the crucial process of harvest and trimming, which ultimately determines the flavor, potency, and overall quality of your harvested cannabis.
Signs of Readiness for Harvest
Before you begin harvesting, it’s important to look for signs that your plants are ready. The timing of harvest plays a vital role in maximizing cannabinoid and terpene production. Keep an eye out for the following indications:
- Trichome Color: The trichomes, which are the resin glands on your buds, change color as they mature. Look for milky or cloudy trichomes and avoid harvesting when they are still clear.
- Pistil Color: The pistils, or the tiny hairs on the buds, will also change color during the flowering stage. Most cultivators choose to harvest when the pistils have turned orange or brown.
- Bud Structure: Pay attention to the overall structure of the buds. They should be dense and well-formed, indicating maturity.
Harvesting Techniques
Once you’ve determined that your plants are ready for harvest, it’s important to choose the right technique for cutting and collecting your buds. Here are some commonly used harvesting methods:
- Selective Harvesting: This method involves selectively harvesting only the mature buds while allowing the rest of the plant to continue flowering.
- Whole Plant Harvesting: With this technique, the entire plant is harvested at once, providing a higher yield but also requiring more time for trimming.
- Staggered Harvesting: Staggered harvesting involves harvesting the top buds when they are ready and allowing the lower buds more time to mature before collecting them.
Importance of Curing and Drying
After harvesting, the curing and drying process is crucial for preserving the flavor, aroma, and potency of your cannabis. Properly cured and dried buds offer a smoother smoking experience and maximize the full potential of terpene profiles. Here are some key steps to follow:
- Trimming: Trim off any excess fan leaves, leaving only the manicured buds.
- Drying: Hang the trimmed buds upside down in a cool, dark, and well-ventilated space. Maintain a temperature of around 60-70°F (15-21°C) and humidity levels around 45-55% to prevent mold and mildew.
- Curing: Once the buds are dry, place them in airtight containers, such as glass jars, and open them daily for the first few weeks to let excess moisture escape. Curing typically lasts for several weeks to enhance flavor and potency.
By following these harvesting, trimming, and curing techniques, you can ensure that your cannabis harvest is of the highest quality, delivering a rewarding experience for both recreational and medicinal users.
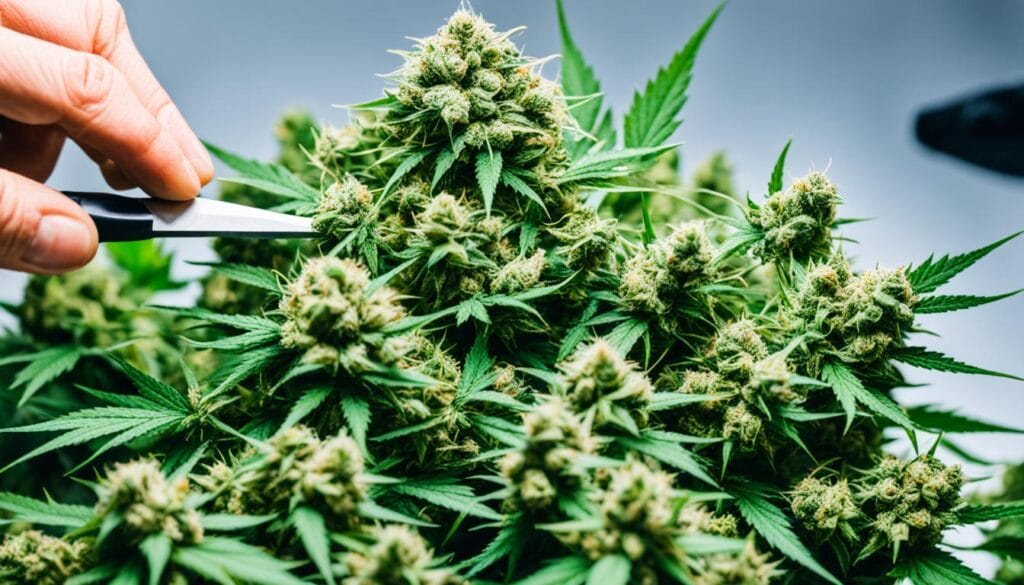

Advanced Techniques in Cannabis Cultivation
As cannabis cultivation continues to evolve, cultivators are constantly exploring advanced techniques to enhance plant growth, increase yields, and optimize overall quality. In this section, we will delve into three key areas of advanced cannabis cultivation: hydroponics, organic cultivation, and supplemental lighting methods.
Hydroponics: Maximizing Nutrient Uptake
Hydroponics is a cultivation method that involves growing plants in a nutrient-rich, water-based solution, without the use of soil. This technique offers several advantages, including improved nutrient uptake, faster growth rates, and increased control over environmental factors.
With hydroponics, cultivators can precisely tailor nutrient solutions to meet the specific needs of cannabis plants at different stages of growth. This allows for optimized nutrient delivery, resulting in healthier plants and higher yields. Additionally, the absence of soil minimizes the risk of pests and diseases.
Hydroponics systems can vary widely, from simple setups using nutrient film technique (NFT) or deep water culture (DWC) to more complex systems like aeroponics or recirculating systems.
Organic Cultivation: Nurturing Sustainable Growth
Organic cultivation focuses on nurturing the cannabis plant using natural and sustainable methods. By harnessing the power of beneficial microbes, compost teas, and organic nutrients, cultivators can promote healthy plant development while minimizing environmental impact.
Organic cultivation boosts soil health, enhances nutrient availability, and improves the overall quality of the final product. It emphasizes the use of organic fertilizers, compost, and natural pest control methods, reducing the reliance on synthetic chemicals.
Through organic cultivation, cultivators can develop a deeper connection with the cannabis plant and the surrounding ecosystem, ensuring that their cultivation practices align with sustainable principles.
Supplemental Lighting: Extending the Growing Season
Supplemental lighting techniques are employed to extend the amount of light cannabis plants receive during their growth stages. By strategically using artificial lighting, cultivators can create optimal growing conditions year-round, regardless of climate or natural sunlight limitations.
Supplemental lighting systems can range from High-Intensity Discharge (HID) lamps, Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs), to ceramic metal halide (CMH) lamps. These systems provide the necessary light intensity and spectrum to support healthy plant growth and maximized crop production.
Using supplemental lighting allows growers to maintain consistent light cycles, promote vigorous vegetative growth, and encourage prolific flowering. This technique is particularly valuable in regions with shorter daylight periods or for indoor cultivation.
| Advanced Cultivation Technique | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Hydroponics |
|
| Organic Cultivation |
|
| Supplemental Lighting |
|
Pests, Diseases, and Plant Health
In any cannabis cultivation journey, it is essential to prioritize plant health and be aware of potential threats posed by pests and diseases. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced grower, understanding how to prevent, detect, and treat these issues is crucial to maintain a thriving cannabis garden.
Pest Prevention
Prevention is key when it comes to pest control. By implementing effective prevention strategies, you can significantly reduce the risk of infestations. Here are some practical tips:
- Practice good hygiene in your grow space, keeping it clean and free of debris.
- Regularly inspect plants for signs of pest activity, such as webbing, discoloration, or chewed leaves.
- Introduce beneficial insects, like ladybugs or predatory mites, to naturally control pests.
- Use physical barriers, such as mesh screens, to keep insects out of your grow area.
- Rotate your crop location to disrupt pest life cycles and reduce the risk of reinfestation.
Early Detection and Diagnosis
Early detection of pest or disease issues is vital for prompt treatment and prevention of further damage. Regular monitoring and attentive observation will help you identify these problems before they escalate.
“Regular monitoring and attentive observation will help you identify these problems before they escalate.”
Treatment Options
If you do encounter pests or diseases in your cannabis garden, there are an array of treatment options available to help nurse your plants back to health:
- Organic insecticides or pesticides can target specific pests while minimizing harm to beneficial insects.
- Fungicides can help combat fungal diseases, such as powdery mildew or gray mold.
- Neem oil, a popular organic treatment, can be effective against a range of pests.
- Biological controls, like predatory insects or beneficial nematodes, can provide long-term pest management.
- Systemic treatments, such as insecticidal drenches or foliar sprays, can be used for more severe infestations.
Remember, it’s essential to thoroughly research and follow the instructions provided for any treatment method to ensure the safety of your plants and yourself.
Plant Health Maintenance
Keeping your cannabis plants healthy and resilient is a critical aspect of preventing pest and disease issues. Here are some general tips to promote plant health:
- Provide proper nutrition with a balanced fertilizer regimen tailored to each growth stage.
- Ensure adequate airflow and ventilation in your grow space to minimize humidity and reduce the risk of mold or mildew.
- Regularly prune plants to remove dead or damaged leaves, promoting better airflow through the canopy.
- Monitor and maintain ideal temperature and humidity levels for optimal plant growth.
- Implement a strict watering schedule to prevent overwatering or underwatering, which can weaken plants and make them more susceptible to diseases.
By following these practices, you can create a robust and resilient environment for your cannabis plants, minimizing the risk of pest and disease issues.
Conclusion
Understanding the various stages of the cannabis plant life cycle is essential for cultivators looking to maximize their yield and quality. From germination to harvest, each stage plays a crucial role in the plant’s overall development and success. By recognizing the importance of proper care, nutrient balance, and environmental conditions, growers can optimize their cultivation practices and achieve thriving, healthy plants.
One significant stage in the cannabis plant’s life cycle is the flowering stage, where the plant undergoes dramatic changes and produces the prized blooms. This is the phase when buds, pistils, and trichomes develop, creating the rich and potent flowers that cannabis enthusiasts seek. By understanding the specific requirements of the flowering stage, such as adjusting light cycles and nutrient ratios, growers can enhance flower quality and ultimately maximize their harvest.
Mastering the different stages of the cannabis plant’s life cycle, including the crucial flowering stage, empowers growers to cultivate high-quality plants with impressive yields. By implementing proper techniques and maintaining a healthy growing environment, cultivators can reap the benefits of their efforts. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced cultivator, understanding and respecting the cannabis plant’s life cycle is key to achieving successful and rewarding harvests.
FAQ
What are the different stages of the cannabis plant life cycle?
The cannabis plant life cycle consists of several stages, including germination, seedling, vegetative growth, transition to flowering, flowering, and harvest.
How does germination occur in cannabis plants?
Germination is the first stage of the cannabis plant life cycle. It involves the sprouting of a seed and the emergence of a young plant. Proper soil conditions, quality seeds, and adequate moisture are important factors for successful germination.
What are the characteristics of the seedling stage?
During the seedling stage, cannabis plants develop their first true leaves and establish a root system. This stage is characterized by fragile and delicate plants that require specific care and environmental conditions to promote healthy growth.
How can I promote vegetative growth in cannabis plants?
To promote vegetative growth in cannabis plants, it is essential to provide them with sufficient light, nutrients, and the right environmental conditions. Pruning and training techniques can also be used to enhance plant structure and maximize yields.
What triggers the transition from vegetative growth to flowering in cannabis plants?
The transition from vegetative growth to flowering in cannabis plants is triggered by changes in the light cycle. When the plants receive a certain amount of uninterrupted darkness, they begin to initiate flowering.
What happens during the flowering stage of the cannabis plant life cycle?
The flowering stage is when cannabis plants develop buds, pistils, and trichomes, which contain the plant’s cannabinoids and terpenes. This stage is crucial for the production of potent and high-quality flowers.
How do I know when to harvest my cannabis plants?
The timing for harvest depends on the desired effects and the strain being cultivated. Generally, the trichomes on the flowers turn cloudy or amber, and the pistils change color. Harvesting at the right time ensures optimal potency and flavor.
What are some advanced techniques in cannabis cultivation?
Advanced techniques in cannabis cultivation include hydroponics, organic cultivation methods, and the use of supplemental lighting. These techniques can help improve plant growth and overall yields.
How can I maintain the health of my cannabis plants and prevent pests and diseases?
Regular monitoring, proper hygiene practices, and preventive measures, such as using beneficial insects, can help maintain the health of cannabis plants. Early detection and appropriate treatment of pests and diseases are crucial to prevent crop loss.
Why is it important to understand each stage of the cannabis plant life cycle?
Understanding each stage of the cannabis plant life cycle is essential for cultivators to provide the right care, nutrients, and environmental conditions at each phase. This knowledge allows growers to optimize cultivation practices and achieve successful and rewarding harvests.
Suggested Articles
;)
;)
;)




 26 Dec 2025
26 Dec 2025  8 min read
8 min read


 February 28, 2024
February 28, 2024 


RESPONSES (0)
No responses yet. Be the first to respond!