Can You Clone Feminized Cannabis Plants?
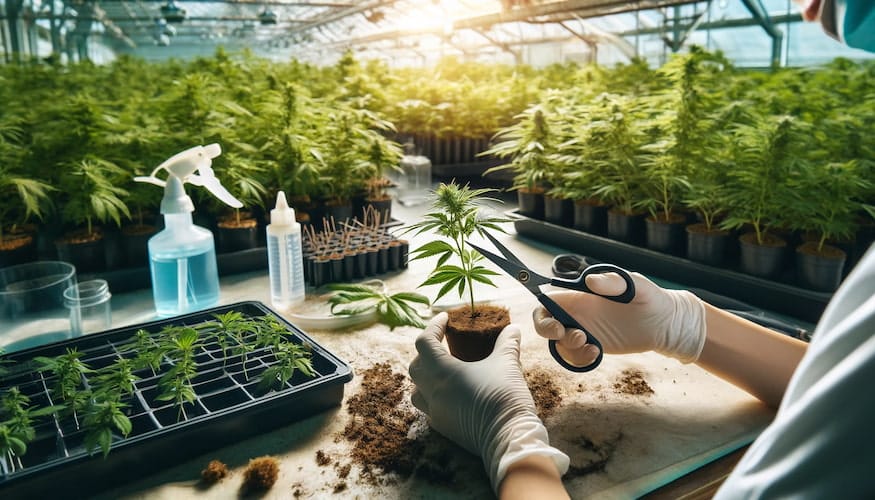

Cloning cannabis plants is a popular method among growers to maintain the genetic consistency of a preferred strain. But what about feminized seeds? Many cultivators wonder if it’s possible and practical to clone plants grown from feminized seeds. The short answer is yes, you can clone feminized seeds, but there are some important considerations and techniques to keep in mind to ensure success.
In this comprehensive article, we’ll describe feminized seeds, examine their genetic makeup, and offer a step-by-step guide to cloning them.
Understanding Feminized Seeds
Before diving into the cloning process, it’s essential to understand what feminized seeds are and how they differ from regular seeds.
Feminized Seeds: These seeds are bred to produce only female plants, which form the buds used for consumption. Female plants are preferred because they produce the cannabinoids desired by both recreational and medicinal users. Feminized seeds are created by inducing a female plant to produce pollen, which is then used to pollinate another female plant. This process results in seeds that carry only female chromosomes.
Regular Seeds: Regular seeds, on the other hand, have a roughly 50/50 chance of producing either male or female plants. While male plants are necessary for breeding new strains, they do not produce consumable buds and are typically removed from the growing area to prevent pollination of the females.
Feminized vs. Regular Seeds: Chromosomes and Gender
One common misconception among cannabis growers is that feminized plants are somehow different from female plants grown from regular seeds. In reality, feminized plants and female plants from regular seeds are essentially the same when it comes to their chromosomes and overall characteristics.
Chromosomes and Gender in Cannabis Plants
Cannabis plants are dioecious, meaning they have distinct male and female plants. The sex of a cannabis plant is determined by its chromosomes:
- Female Plants: Female cannabis plants have two X chromosomes (XX). These plants are the ones that produce the buds used for consumption.
- Male Plants: Male cannabis plants have one X and one Y chromosome (XY). They produce pollen needed for breeding but do not produce consumable buds.
When we talk about feminized seeds, we’re referring to seeds that have been specially bred to contain only female chromosomes (XX). This breeding process ensures that nearly all the plants grown from feminized seeds will be female, which is highly desirable for growers focused on bud production.
Comparing Feminized Seeds and Regular Seeds
- Feminized Seeds: These are produced by causing a female plant to produce pollen, which is then used to fertilize another female plant. This results in seeds that carry only female (XX) chromosomes. Feminized seeds are specifically designed to eliminate the male chromosomes, thereby ensuring that nearly all the plants will be female.
- Regular Seeds: These seeds are produced by the natural pollination process involving a male and a female plant. Regular seeds have a roughly 50/50 chance of being either male or female. The female plants from regular seeds will have the same (XX) chromosomes as those from feminized seeds.
Key Point: Chromosomal Identity
The critical point to understand is that a female plant grown from feminized seeds is chromosomally identical to a female plant grown from regular seeds. Both have the same (XX) chromosomes and, consequently, the same potential for breeding, cloning, and bud production.
Practical Implications for Growers
For growers, this means that feminized seeds offer a reliable way to ensure a female-only crop without any compromise in the quality or characteristics of the plants. Feminized plants will grow, flower, and produce buds in the same manner as female plants grown from regular seeds.
This consistency is a significant advantage, as it removes the need to identify and remove male plants, which can pollinate females and reduce the quality and quantity of the bud harvest. By using feminized seeds, growers can focus on nurturing their plants and optimizing their growing conditions to achieve the best possible yield and potency.

Benefits of Cloning Feminized Seeds
Cloning feminized seeds can be beneficial for several reasons:
- Consistency: Cloning ensures that the genetic makeup of the plant remains consistent, providing the same flavor, potency, and growth characteristics with each new plant.
- Efficiency: Cloning eliminates the need for germination and early seedling care, saving time and effort.
- Predictability: With clones, growers know exactly what to expect regarding plant characteristics, growth habits, and yield.
The Cloning Process
Cloning cannabis plants, whether from feminized or regular seeds, involves taking a cutting from a healthy mother plant and encouraging it to develop roots. Here’s a step-by-step guide to successfully clone your feminized cannabis plants.
1. Selecting the Mother Plant
Choosing the right mother plant is crucial. Look for the following traits in your mother plant:
- Health: The mother plant should be healthy, free of pests and diseases, and exhibit vigorous growth.
- Desirable Traits: Ensure the plant has the characteristics you want to preserve, such as high yield, potent buds, and robust flavor.
- Maturity: The mother plant should be mature enough to produce viable cuttings. Typically, this means it should be at least two months old.
2. Preparing for Cloning
Before taking cuttings, gather all necessary materials:
- Sharp, Sterile Cutting Tool: A razor blade or sharp scissors sterilized with alcohol.
- Rooting Hormone: This helps stimulate root growth. It comes in powder, gel, or liquid form.
- Cloning Medium: Rockwool cubes, peat pellets, or a cloning machine.
- Humidity Dome: To maintain high humidity levels, which are crucial for successful rooting.
- Spray Bottle: Filled with water to keep the cuttings moist.
3. Taking Cuttings
Follow these steps to take cuttings from your feminized mother plant:
- Select a Branch: Choose a healthy branch with several nodes (the points where leaves and branches grow from the stem).
- Make the Cut: Using your sterile cutting tool, make a 45-degree cut below a node. Aim for a cutting that’s 4-6 inches long.
- Remove Lower Leaves: Trim away the leaves from the bottom half of the cutting, leaving the top few leaves intact.
- Dip in Rooting Hormone: Immediately dip the cut end into the rooting hormone to promote root development.
4. Planting the Cuttings
Next, plant the cuttings in your chosen cloning medium:
- Prepare the Medium: If using rockwool cubes or peat pellets, soak them in water and let them drain until they are moist but not waterlogged.
- Insert the Cutting: Gently insert the cut end of the cutting into the medium, ensuring it’s stable and upright.
- Place in Humidity Dome: Put the planted cuttings under a humidity dome to maintain high humidity levels, which helps prevent the cuttings from drying out.
5. Caring for the Clones
Proper care during the first few weeks is crucial for successful rooting:
- Humidity: Keep the humidity levels high (around 70 to 80%) using the humidity dome.
- Light: Provide gentle, indirect light. Too much light can stress the cuttings.
- Temperature: Maintain a temperature range of 70 to 75°F (21-24°C).
- Moisture: Keep the medium moist but not soggy. Use a spray bottle to mist the cuttings regularly.
Rooting Timeline and Transplanting
Roots typically begin to form within 7 to 14 days, but some cuttings can take up to three weeks. Here’s how to check for roots and proceed with transplanting:
- Check for Roots: Gently tug on the cuttings after a week or two. If you feel resistance, roots are forming.
- Transplanting: Once roots are well-developed, transplant the clones into larger pots with your preferred growing medium (soil, coco coir, or hydroponics).
Cloning Best Practices
To maximize your success with cloning feminized seeds, follow these best practices:
- Sanitize Everything: Cleanliness is crucial to prevent infections. Sterilize your tools and work area before taking cuttings.
- Healthy Mother Plants: Only take cuttings from healthy, pest-free mother plants.
- Maintain Optimal Conditions: Consistent humidity, temperature, and light are key to successful rooting.
- Monitor and Adjust: Keep a close eye on your cuttings and adjust environmental conditions as needed.
Advanced Cloning Techniques
For those looking to refine their cloning process, here are some advanced techniques:
- Air Layering: This involves creating a wound on the plant stem while it’s still attached to the mother plant and encouraging roots to form at the wound site before cutting it off. This method can be more successful for some growers.
- Tissue Culture: A more advanced method that involves taking a small piece of plant tissue and growing it in a sterile, nutrient-rich environment. This technique can produce many clones from a small amount of plant material and is useful for preserving genetics over long periods.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Cloning cannabis can come with its set of challenges. Here are some common issues and how to address them:
- Wilting Cuttings: If your cuttings are wilting, it could be due to low humidity. Ensure the humidity dome is in place and mist the cuttings regularly.
- Slow Root Development: Rooting can be slow if the temperature is too low or the light is too intense. Adjust the environment to ensure optimal conditions.
- Fungal Growth: Excessive moisture can lead to fungal growth. Ensure the medium is moist but not waterlogged and provide adequate ventilation.

Advantages of Cloning Over Growing From Seed
Cloning feminized seeds offers several advantages over growing from seeds:
- Uniformity: Clones produce identical plants with consistent traits, whereas seeds can result in variable phenotypes.
- Speed: Cloning bypasses the germination and seedling stages, reducing the overall growing time.
- Cost-Effective: While purchasing seeds can be expensive, cloning allows you to perpetuate a single plant without needing to buy new seeds.
Potential Drawbacks of Cloning Feminized Seeds
Despite the benefits, there are some potential drawbacks to consider:
- Genetic Drift: Over time, clones can accumulate genetic mutations, leading to changes in the plant’s characteristics.
- Vigor: Some growers believe plants grown from seeds are more vigorous and resilient than clones.
- Dependency on a Healthy Mother Plant: The success of cloning depends on the health and vitality of the mother plant. If the mother plant is compromised, so will be the clones.
Cloning Equipment and Tools
Investing in the right tools and equipment can improve your cloning success rate. Here are some essentials:
- Cloning Machine: An automated device that provides an optimal environment for cuttings to root.
- Rooting Gel: Specifically designed for cloning, this gel can enhance root development.
- Heat Mat: Helps maintain consistent soil temperatures, which is crucial for root development.
- Humidity Dome with Vents: Allows you to control the humidity levels around your clones.
Legal Considerations
Before you start cloning cannabis, it’s important to be aware of the legal implications:
- Legality: Ensure that cloning and growing cannabis are legal in your area. Laws vary widely by region and country.
- Licensing: In some places, you may need a license to grow cannabis, even for personal use. Check local regulations to ensure compliance.
Conclusion: Cloning Feminized Seeds Is Possible and Practical
Cloning feminized seeds is not only possible but also a practical approach to maintaining genetic consistency, saving time, and ensuring predictability in your cannabis garden. By understanding the cloning process, selecting the right mother plant, and providing optimal conditions, you can successfully clone your favorite feminized cannabis plants. Whether you’re a novice grower or an experienced cultivator, mastering the art of cloning can elevate your cannabis cultivation game, offering you continuous harvests of high-quality, consistent plants.
Now that you know all about cloning feminized cannabis plants, shop the collection of regular, feminized, and autoflower cannabis seeds at Seeds Here Now.
FAQ: Cloning Feminized Seeds
1. Can you clone feminized seeds? Yes, you can clone plants grown from feminized seeds. The process involves taking cuttings from a healthy mother plant and encouraging them to root.
2. Are clones identical to the mother plant? Yes, clones are genetically identical to the mother plant, ensuring consistency in traits such as flavor, potency, and growth habits.
3. Is cloning feminized seeds better than growing from seeds? Cloning offers advantages such as uniformity, faster growth, and cost savings. However, growing from seeds can produce more vigorous plants while avoiding potential genetic drift in clones.
4. What are the ideal conditions for cloning cannabis? Optimal conditions include high humidity (70-80%), gentle indirect light, temperatures of 70-75°F (21-24°C), and a moist but not waterlogged growing medium.
5. How long does it take for clones to root? Roots typically begin to form within 7-14 days, but it can take up to three weeks for some cuttings.
6. What are common problems when cloning cannabis? Common issues include wilting cuttings, slow root development, and fungal growth. These can often be mitigated by maintaining proper humidity, light, temperature, and ventilation.
7. Can I clone any cannabis plant? Yes, but it’s best to clone healthy, mature plants that exhibit desirable traits. Avoid cloning from stressed or unhealthy plants.
8. What equipment do I need for cloning? Essential tools include a sharp, sterile cutting tool, rooting hormone, a cloning medium (such as rockwool cubes), a humidity dome, and a spray bottle.
9. How many times can you clone from a mother plant? A healthy mother plant can produce numerous clones over its lifetime. Regular pruning and proper care can keep a mother plant productive for an extended period.
10. Is cloning cannabis legal? Laws regarding cloning and growing cannabis vary by region. Ensure you understand and comply with local regulations before starting your cloning project.
Suggested Articles
;)
;)
;)




 28 Jan 2026
28 Jan 2026  6 min read
6 min read


 June 12, 2024
June 12, 2024 


RESPONSES (0)
No responses yet. Be the first to respond!