How To Grow Cannabis in a Greenhouse: A Complete Guide
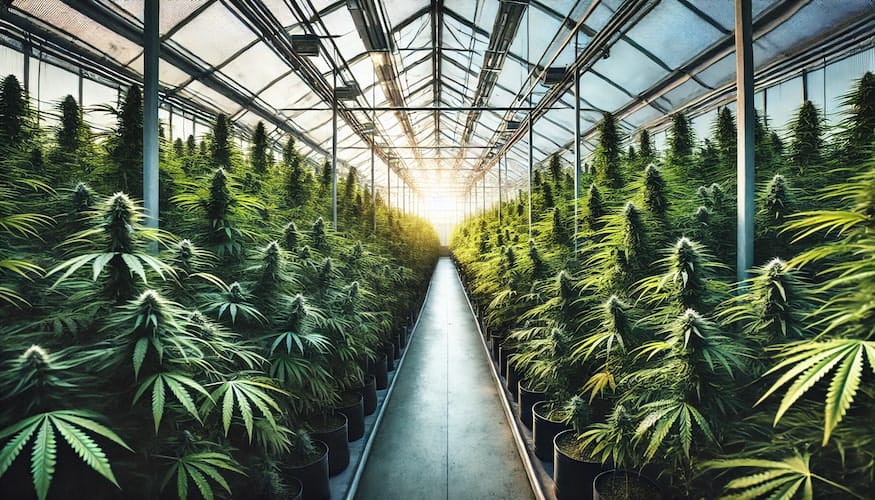

Growing cannabis in a greenhouse offers the best of both indoor and outdoor cultivation methods, allowing you to harness natural sunlight while controlling environmental conditions. Greenhouses provide a protected environment that can extend the growing season, improve plant health, and increase yields. This comprehensive guide will take you through every step of growing cannabis in a greenhouse, from choosing the right structure to harvesting and curing your crop.
Benefits of Greenhouse Cultivation
Before diving into the specifics of greenhouse growing, it’s important to understand the benefits this method offers:
Controlled Environment
Greenhouses allow you to control temperature, humidity, and other environmental factors more effectively than outdoor growing. This control helps prevent common issues like mold, pests, and extreme weather damage. For example, shade cloths and ventilation systems can prevent heat stress, while heaters can protect plants from unexpected frosts.
Extended Growing Season
Greenhouses can extend the growing season by protecting plants from early frosts and allowing for earlier planting in the spring. This extended season can lead to multiple harvests per year, maximizing your yield. For instance, in regions with harsh winters, greenhouses can enable a spring and a fall harvest, effectively doubling your production capability.
Natural Sunlight
Using natural sunlight reduces the need for artificial lighting, which can be expensive and energy-intensive. Sunlight is also more beneficial for plants as it provides a full spectrum of light that is hard to replicate with artificial light. Additionally, plants grown under natural sunlight often exhibit stronger growth and more robust terpene profiles.
Increased Privacy
For growers concerned about privacy, greenhouses offer a discreet way to cultivate cannabis. The structure can shield plants from view and help comply with local regulations. This is particularly useful in areas where outdoor growing is restricted or where discretion is necessary to avoid theft or legal issues.
Improved Plant Health
Greenhouses can create an ideal growing environment that reduces stress on plants and promotes healthy, vigorous growth. The controlled conditions can also lead to higher yields and better-quality buds. For example, maintaining consistent humidity levels can prevent mold and mildew, while controlled temperatures can optimize photosynthesis and growth rates.
Choosing the Right Cannabis Greenhouse
The first step in growing cannabis in a greenhouse is selecting the right structure. Several types of greenhouses are suitable for cannabis cultivation, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
Cold-Frame Greenhouses
Cold-frame greenhouses are simple, low-cost structures made from a frame covered with a transparent material like plastic or glass. They rely on sunlight to warm the interior and are best suited for moderate climates. Cold frames are typically used to extend the growing season by protecting plants from early frosts in spring and late frosts in fall.
Hoop Houses
Hoop houses are semicircular structures made from metal or PVC pipes covered with plastic sheeting. They are more durable than cold frames and can be equipped with ventilation systems to control temperature and humidity. Hoop houses are popular among small-scale growers due to their affordability and ease of construction.
Polycarbonate Greenhouses
Polycarbonate greenhouses use twin-wall polycarbonate panels to create a more insulated environment. These greenhouses offer better temperature control and are more durable than plastic-covered structures. Polycarbonate panels diffuse light more evenly, reducing the risk of hot spots that can burn plants.
Glass Greenhouses
Glass greenhouses are the most durable and provide excellent light transmission. They are more expensive to build and maintain but offer superior environmental control and longevity. Glass greenhouses are ideal for serious growers who plan to cultivate cannabis long-term and require precise environmental control.
Geodesic Dome Greenhouses
Geodesic dome greenhouses are spherical structures that offer excellent light distribution and structural strength. They are more complex to build but can withstand extreme weather conditions. The unique shape of geodesic domes allows for better air circulation and more even heat distribution, making them highly efficient.
Key Considerations
- Size: Choose a greenhouse size that fits your growing goals and available space. Ensure there is enough room for plants to grow and for you to move around and tend to them. Consider the height of the greenhouse, especially if you plan to grow tall sativa strains.
- Materials: Consider the durability and insulation properties of the materials used in the greenhouse construction. Polycarbonate and glass offer better insulation than plastic sheeting. The choice of materials will also affect the greenhouse’s longevity and maintenance requirements.
- Ventilation: Proper ventilation is crucial to control temperature and humidity. Look for greenhouses with adjustable vents or consider adding fans and exhaust systems. Automated ventilation systems can help maintain optimal conditions without constant manual adjustments.
- Budget: Determine your budget and balance the cost of the greenhouse with its features and benefits. Investing in a high-quality greenhouse may have a higher upfront cost but can save money in the long run by reducing energy costs and increasing yields.
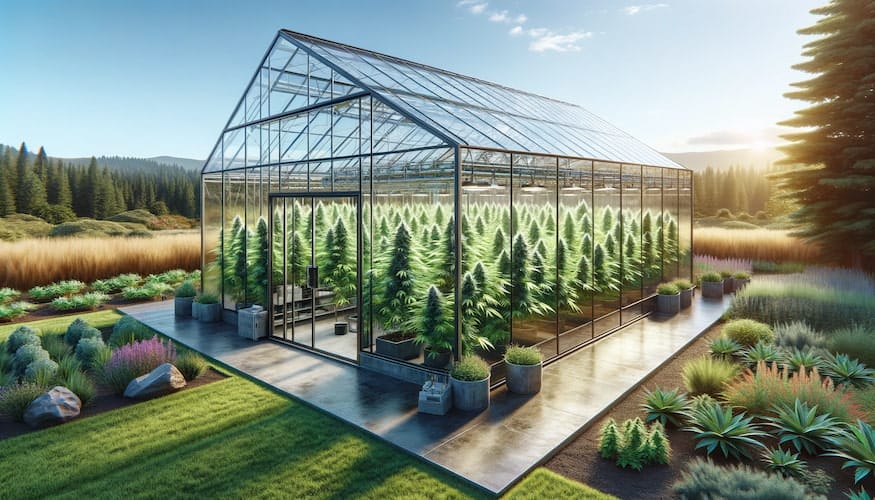

Selecting the Right Location for a Cannabis Greenhouse
Choosing the right location for your greenhouse is a crucial step in ensuring the success of your cannabis cultivation. The location will affect various factors such as light exposure, temperature control, accessibility, and overall plant health. Here are key considerations to help you select the ideal spot for your greenhouse:
Sunlight Exposure
Optimal Sunlight: Cannabis plants thrive on ample sunlight, which is essential for photosynthesis and healthy growth. Ideally, your greenhouse should be located in an area that receives full sun for at least six to eight hours a day. Southern exposure is typically best in the Northern Hemisphere, as it maximizes sunlight during the day.
Avoiding Shade: Ensure the greenhouse is not shaded by tall trees, buildings, or other structures, especially during peak sunlight hours. Shaded areas can reduce light intensity and negatively impact plant growth and yield.
Wind Protection
Sheltered Spot: While good ventilation is important, excessive wind can damage plants and disrupt temperature and humidity control. Choose a location that offers some natural wind protection, such as behind a hedge, fence, or building.
Windbreaks: If natural wind protection is not available, consider installing windbreaks such as fences or rows of shrubs to shield the greenhouse from strong winds. This will help maintain a stable internal environment and protect your plants.
Accessibility
Ease of Access: Select a location that is easily accessible for daily maintenance, watering, feeding, and harvesting. The convenience of access will save time and effort in managing your cannabis plants.
Proximity to Utilities: Ensure the greenhouse is near essential utilities such as water and electricity sources. This proximity will facilitate the installation of irrigation systems, heaters, fans, and lighting if needed.
Ground Conditions
Level Ground: Choose a flat, level area to set up your greenhouse. Uneven ground can lead to structural instability and drainage issues. If the ground is not naturally level, consider grading it before construction.
Soil Quality: If you plan to plant directly into the ground within the greenhouse, ensure the soil is of high quality and well-draining. Conduct a soil test to determine its suitability for cannabis cultivation and amend it if necessary.
Water Drainage
Good Drainage: Ensure the selected location has good drainage to prevent waterlogging, which can lead to root rot and other issues. Avoid low-lying areas that are prone to flooding.
Rainwater Management: Consider the potential for rainwater runoff from nearby structures. Installing gutters and downspouts on the greenhouse can help manage rainwater effectively and prevent water accumulation around the base.
Privacy and Security
Privacy: If you are concerned about privacy, choose a discreet location that is not easily visible from neighboring properties or public areas. Privacy can help protect your crop from theft and comply with local regulations regarding cannabis cultivation.
Security Measures: Implement additional security measures such as fencing, locks, and surveillance cameras to safeguard your greenhouse and its contents. A well-secured location will provide peace of mind and protect your investment.
Climate Considerations
Microclimate: Consider the microclimate of the selected area. Factors such as temperature fluctuations, humidity levels, and frost pockets can vary within a property and affect plant health. Choose a location with a favorable microclimate for cannabis cultivation.
Local Climate: Learn about your region’s broader climate conditions, including seasonal temperature ranges, precipitation patterns, and potential weather extremes. This knowledge will help you prepare and equip your greenhouse accordingly.
Future Expansion
Space for Growth: If you plan to expand your cultivation efforts in the future, select a location that allows for the potential enlargement of your greenhouse or the addition of multiple structures. This foresight can save time and resources in the long run.
By carefully considering these factors, you can select the optimal location for your greenhouse, ensuring a successful and productive cannabis cultivation experience. A well-chosen location will provide the necessary environmental conditions for your plants to thrive, leading to healthier growth and higher yields.
Preparing the Cannabis Greenhouse
Once you have chosen and set up your greenhouse, it’s time to prepare it for cannabis cultivation. This involves creating an optimal environment for your plants to thrive.
Lighting
While greenhouses rely primarily on natural sunlight, supplemental lighting can be beneficial on cloudy days or to extend the daylight hours in early spring or late fall.
- Types of Lights: LED grow lights are energy-efficient and provide a full spectrum of light. High-Intensity Discharge (HID) lights, including Metal Halide (MH) and High-Pressure Sodium (HPS) lights, are also popular for their intensity and effectiveness. LED lights generate less heat, which can be advantageous in warmer climates.
- Lighting Schedule: Cannabis plants require 18 to 24 hours of light per day during the vegetative stage. In the flowering stage, reduce this to 12 hours of light per day to trigger bud development. Using timers can help maintain consistent light schedules without manual intervention.
Temperature Control
Maintaining a consistent temperature is crucial for healthy cannabis growth. Cannabis thrives in temperatures between 70 and 85 degrees Fahrenheit (21-29°C) during the day and 60 to 70 degrees Fahrenheit (15-21°C) at night.
- Heating: In colder climates, you may need to add heaters to maintain optimal temperatures, especially at night or in early spring. Consider using propane or electric heaters with thermostats for precise temperature control.
- Cooling: In hot climates, shade cloths, ventilation fans, and evaporative coolers can help keep temperatures in check. Automated vent openers can help regulate temperature by opening and closing vents as needed.
Humidity Control
Cannabis plants prefer a relative humidity (RH) of 40 to 70 percent. High humidity can lead to mold and mildew, while low humidity can stress plants.
- Humidity During Vegetative Stage: Keep RH between 60 to 70 percent. Higher humidity levels support vigorous vegetative growth by facilitating nutrient uptake and reducing water stress.
- Humidity During Flowering Stage: Reduce RH to 40 to 50 percent to prevent mold and bud rot. Lower humidity levels help prevent the development of fungal diseases that can devastate your crop.
Ventilation
Proper ventilation is essential for controlling temperature and humidity and ensuring a fresh supply of CO2 for your plants.
- Exhaust Fans: Install exhaust fans to remove hot air and bring in fresh air. Position the fans at the highest point in the greenhouse to efficiently remove rising hot air.
- Oscillating Fans: Use oscillating fans to circulate air within the greenhouse and strengthen plant stems. Proper air circulation helps prevent hot spots and reduces the risk of mold and pests.
Soil and Containers
Choosing the right soil and containers is critical for healthy root development and nutrient uptake.
- Soil: Use a high-quality, well-draining soil mix specifically formulated for cannabis. You can also use soilless mixes like coco coir or peat moss. Amending the soil with organic matter like compost or worm castings can improve fertility and structure.
- Containers: Fabric pots or air pots promote better root aeration and prevent root-bound plants. Choose containers that are large enough to support the size of your plants. Larger containers provide more space for root growth, leading to healthier and more productive plants.
Selecting and Germinating Cannabis Seeds
The next step is selecting the right cannabis seeds and germinating them.
Choosing Seeds
- Strain Selection: Choose strains that are well-suited for greenhouse growing and your climate. Indica strains tend to be shorter and more bushy, while sativa strains are taller and more suited for larger greenhouses. Hybrid strains can offer a balance of traits from both indica and sativa.
- Feminized Seeds: Feminized seeds ensure that all plants will be female, which are the ones that produce buds. This eliminates the need to identify and remove male plants, simplifying the growing process.
- Autoflower Seeds: Autoflower seeds are easier to grow and have a shorter life cycle, making them ideal for beginners. They automatically switch from the vegetative stage to the flowering stage based on age, not light schedule.
Germination Methods
- Paper Towel Method: Place seeds between damp paper towels, then place them in a plastic bag or container. Keep them warm and dark until they sprout. This method allows you to monitor the seeds closely and ensures a high germination rate.
- Direct Planting: Plant seeds directly into the soil or starter plugs. Keep the soil moist and warm until the seeds sprout. This method reduces the risk of damaging delicate seedlings during transplanting.
Transplanting Seedlings
Once the seedlings have developed a few sets of leaves, they can be transplanted into larger containers or directly into the greenhouse soil.
- Handling Seedlings: Handle seedlings carefully to avoid damaging the delicate roots. Use a gentle touch and support the stem to prevent stress.
- Planting Depth: Plant seedlings at the same depth they were in the starter medium. Planting too deep can stress the seedlings and slow their growth.
- Watering: Water the seedlings immediately after transplanting and keep the soil moist but not waterlogged. Proper watering helps the seedlings establish strong roots and reduces transplant shock.
Vegetative Stage
During the vegetative stage, cannabis plants focus on growing leaves and stems. This stage lasts anywhere from 3 to 16 weeks, depending on the strain and growing conditions.
Lighting
Ensure your plants receive at least 18 hours of light per day. If natural light is insufficient, supplement with grow lights. Consistent lighting encourages vigorous vegetative growth and prepares the plants for a successful flowering stage.
Nutrients
Cannabis plants require different nutrients at different stages of growth. During the vegetative stage, focus on providing higher levels of nitrogen, which supports leafy growth.
- Nitrogen (N): Essential for leaf and stem growth. Nitrogen is a key component of chlorophyll, the molecule responsible for photosynthesis.
- Phosphorus (P): Supports root development and is crucial for energy transfer and storage within the plant.
- Potassium (K): Promotes overall plant health. Potassium helps regulate water uptake, enzyme activation, and resistance to diseases.
Watering
Keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. Overwatering can lead to root rot while underwatering can stress the plants and stunt their growth. Monitor the moisture levels by checking the soil regularly and adjusting your watering schedule as needed.
Training Techniques
Training techniques can help maximize yields and manage plant growth.
- Topping: Cut off the main shoot to encourage the growth of multiple colas. This technique helps create a bushier plant with more bud sites.
- LST (Low-Stress Training): Bend and tie down branches to create an even canopy. LST improves light penetration and airflow, leading to healthier plants and higher yields.
- SCROG (Screen of Green): Use a screen or net to spread out the branches and ensure even light distribution. SCROG maximizes the use of available light and space, promoting uniform bud development.
Pest and Disease Management
Keep an eye out for common pests and diseases. Regularly inspect your plants and take action at the first sign of trouble.
- Pests: Aphids, spider mites, whiteflies, and caterpillars. Use organic pest control methods like neem oil, insecticidal soap, or introducing beneficial insects.
- Diseases: Powdery mildew, bud rot, and root rot. Maintain proper humidity levels, ensure good air circulation, and remove infected plant material promptly.
Flowering Stage
The flowering stage is when cannabis plants produce buds. Depending on the strain, this stage lasts 6 to 12 weeks.
Lighting
Reduce the light schedule to 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness to trigger flowering. Consistent light schedules are crucial for inducing and maintaining the flowering process.
Nutrients
Switch to a bloom-specific nutrient formula with higher levels of phosphorus and potassium to support bud development.
- Phosphorus (P): Essential for bud formation. Phosphorus supports energy transfer and genetic material synthesis, crucial for flower development.
- Potassium (K): Supports overall plant health and bud density. Potassium helps regulate water uptake, enzyme activation, and resistance to diseases.
Watering
Water needs may increase during the flowering stage. Ensure the soil remains moist but not waterlogged. Proper watering supports the plants’ increased metabolic activity during bud formation.
Humidity and Ventilation
Reduce humidity to 40 to 50 percent to prevent mold and bud rot. Ensure good air circulation with fans and exhaust systems. Proper humidity control and ventilation are critical for maintaining healthy buds.
Supporting Buds
As buds grow larger, they may need support to prevent branches from breaking.
- Stakes: Use stakes to support heavy branches. Stakes help keep branches upright and prevent damage from the weight of the buds.
- Trellising: Use a trellis or netting to support and spread out branches. Trellising improves light penetration and air circulation, promoting healthier bud development.
Pest and Disease Management
Continue monitoring for pests and diseases. Pay special attention to mold and bud rot, which can ruin your harvest. Regularly inspect your plants and take preventative measures to maintain a healthy crop.
Harvesting and Curing Cannabis
Knowing when and how to harvest and cure your cannabis is crucial for maximizing potency, flavor, and overall quality.
Determining Harvest Time
Harvest time depends on the strain and growing conditions. Look for the following signs to determine when to harvest:
- Trichome Color: Use a magnifying glass to inspect the trichomes. Harvest when they are milky white with some turning amber. This indicates the peak potency and desired effects.
- Pistil Color: Look for pistils (hairs) that have turned from white to orange or brown. This change in color indicates that the buds are mature and ready for harvest.
Harvesting Techniques
- Cutting: Use sharp, clean scissors to cut branches or individual buds. Sharp tools minimize damage to the plant and reduce the risk of introducing pathogens.
- Trimming: Remove large fan leaves and smaller sugar leaves. You can do a wet trim (immediately after harvest) or a dry trim (after drying). Proper trimming enhances the buds’ appearance and quality.
Drying
Drying is essential to remove moisture from the buds and prevent mold.
- Hanging: Hang branches or individual buds upside down in a dark, well-ventilated room. Ensure there is adequate space between the buds for air circulation.
- Drying Time: Drying usually takes 7 to 14 days, depending on humidity and temperature. The buds should feel dry to the touch and stems should snap easily. Proper drying preserves the potency and flavor of the cannabis.
Curing
Curing improves the flavor and potency of your cannabis.
- Jars: Place dried buds in airtight glass jars. Glass jars prevent contamination and allow for controlled curing conditions.
- Burping: Open the jars for a few minutes each day to release moisture and allow fresh air in. This process should be done for the first one to two weeks. Burping prevents mold growth and promotes even drying.
- Curing Time: Cure the buds for at least two to four weeks, though longer curing times (up to six months) can further enhance quality. Proper curing enhances the terpene profile and smoothness of the smoke.
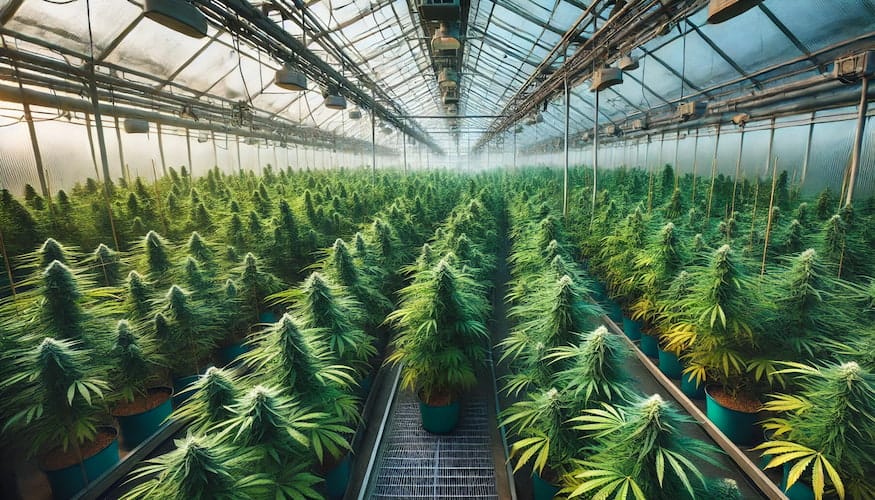

Light Deprivation (“Light Dep”) Techniques for Greenhouse Cannabis Cultivation
Light deprivation, commonly referred to as “light dep,” is a powerful technique used in greenhouse cannabis cultivation to control the photoperiod of plants. This method involves manipulating the amount of light your plants receive to simulate the natural light cycles of different seasons, thereby inducing flowering at specific times. Light dep techniques can help growers achieve multiple harvests per year, optimize yield quality, and improve overall plant health. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to implement light dep in your greenhouse.
Understanding Light Dep Techniques
Light dep involves covering your greenhouse to block out light during part of the day, reducing the hours of light your plants receive. By controlling the light exposure, you can trigger the flowering stage of cannabis plants earlier than they would under natural light conditions. This technique is particularly beneficial for growers who want to produce high-quality buds outside the traditional outdoor growing season.
Benefits of Light Dep Techniques
Multiple Harvests Per Year: By controlling the light cycle, you can force your plants to flower multiple times within a single year, significantly increasing your overall yield.
Enhanced Quality: Light dep allows you to harvest during optimal conditions, avoiding the challenges of late-season pests, mold, and weather issues. This can result in higher quality and more potent buds.
Consistency and Predictability: With light dep, you can schedule your harvests more precisely, ensuring a steady supply of cannabis throughout the year.
Pest and Disease Management: Early flowering and harvests can help avoid peak seasons for pests and diseases, reducing the risk of crop damage.
Implementing Light Dep Techniques
To effectively use light dep techniques, you need to create a controlled environment that allows you to manipulate the light cycle. Here are the steps to implement light dep in your greenhouse:
Choosing the Right Greenhouse Covering
Lightproof Coverings: Use blackout tarps or lightproof fabrics specifically designed for light dep. These materials are durable, UV-resistant, and completely block out light when deployed.
Automated Systems: Consider investing in automated light dep systems that use motors and timers to deploy and retract the blackout coverings. Automated systems ensure precise light control and reduce the labor involved in manual covering.
Light Dep Schedule
Vegetative Stage: During the vegetative stage, cannabis plants require 18 to 24 hours of light per day. Ensure your greenhouse allows for maximum sunlight exposure during this period. Supplemental lighting may be used to extend daylight hours if needed.
Flowering Stage: To induce flowering, reduce the light exposure to 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness each day. Use the blackout coverings to create the necessary dark period. This change in light schedule will trigger the flowering hormones in your cannabis plants.
Managing Light Deprivation
Consistency: Maintain a consistent light dep schedule to avoid stressing the plants. Inconsistent light cycles can lead to hermaphroditism or reduced yields.
Timing: Ensure the blackout coverings are deployed and retracted at the same times each day. Use timers to automate this process for accuracy and convenience.
Ventilation: Proper ventilation is crucial during the dark period to prevent mold and mildew. Ensure your greenhouse has adequate airflow, even when covered. Use fans and ventilation systems to maintain air circulation and humidity levels.
Monitoring and Adjusting
Environmental Control: Continuously monitor the temperature and humidity inside the greenhouse, especially during the dark period. Sudden changes can stress plants and impact growth.
Plant Health: Regularly inspect your plants for signs of stress or disease. Light dep techniques can increase the risk of mold and mildew if not managed properly.
Adjustments: Be prepared to adjust your light dep schedule based on plant responses and environmental conditions. Flexibility is key to successful light dep implementation.
Harvesting with Light Dep
Staggered Harvests: Plan your light dep schedule to stagger harvests. This approach ensures a continuous supply of fresh cannabis and allows you to manage drying and curing processes more efficiently.
Quality Control: Harvesting under optimal conditions, such as avoiding high humidity and pest-prone periods, can enhance the quality and potency of your cannabis.
Challenges and Solutions
Manual Labor: Manually deploying and retracting blackout coverings can be labor-intensive. Solution: Invest in automated light dep systems to reduce labor and ensure consistency.
Ventilation Issues: Inadequate ventilation during the dark period can lead to mold and mildew. Solution: Use fans and ventilation systems to maintain airflow and control humidity levels.
Light Leaks: Even small light leaks can disrupt the flowering cycle. Solution: Regularly inspect your greenhouse for light leaks and repair any gaps or holes in the covering.
Light deprivation techniques offer a powerful tool for greenhouse cannabis growers, enabling them to control the photoperiod and optimize harvest times. By implementing light dep, you can achieve multiple harvests per year, improve the quality of your buds, and manage environmental challenges more effectively. With careful planning and management, light dep can significantly enhance your greenhouse cannabis cultivation experience, leading to healthier plants and higher yields.
Troubleshooting Common Issues in the Greenhouse
Growing cannabis in a greenhouse can present unique challenges. Here are some common issues and how to address them:
Temperature Fluctuations
- Issue: Temperature swings can stress plants and affect growth.
- Solution: Use heaters or cooling systems to maintain consistent temperatures. Consider using shade cloths during hot days and insulating the greenhouse during cold nights. Automated climate control systems can help maintain optimal conditions.
High Humidity
- Issue: High humidity can lead to mold and mildew.
- Solution: Use dehumidifiers and ensure good ventilation. Reduce watering frequency and improve air circulation with fans. Regularly monitor humidity levels and adjust as needed to prevent fungal diseases.
Pest Infestations
- Issue: Pests can damage plants and reduce yields.
- Solution: Regularly inspect plants and use organic pest control products such as neem oil or insecticidal soap. Introduce beneficial insects like ladybugs to control pests naturally. Maintain a clean growing environment to reduce the risk of infestations.
Nutrient Deficiencies
- Issue: Yellowing leaves, stunted growth, and other symptoms can indicate nutrient deficiencies.
- Solution: Ensure a balanced nutrient regimen and adjust feeding schedules as needed. Test soil pH regularly and adjust it to ensure optimal nutrient uptake. Use foliar feeding to address deficiencies quickly and effectively.
Poor Air Circulation
- Issue: Poor air circulation can lead to mold and weak plant growth.
- Solution: Use oscillating fans to improve air movement within the greenhouse. Ensure exhaust fans are functioning properly to remove stale air and bring in fresh air. Proper ventilation prevents hot spots and supports healthy plant growth.
Growing Cannabis in a Greenhouse: Conclusion
Growing cannabis in a greenhouse offers numerous benefits, including controlled environmental conditions, extended growing seasons, and increased privacy. By choosing the right greenhouse, preparing it properly, and following best practices for lighting, temperature, humidity, and nutrient management, you can achieve healthy, high-yielding cannabis plants. Remember to monitor for pests and diseases, use training techniques to maximize yields, and harvest and cure your buds correctly to ensure the highest quality product.
With the right approach and attention to detail, greenhouse cultivation can be a rewarding and productive way to grow cannabis. Happy growing!
Now that you know how to grow cannabis in a greenhouse, get your garden started by shopping the collection of regular, feminized, and autoflower cannabis seeds at Seeds Here Now.
FAQs
1. What are the benefits of growing cannabis in a greenhouse?
Growing cannabis in a greenhouse offers several advantages, including a controlled environment, extended growing seasons, natural sunlight exposure, increased privacy, and improved plant health. Greenhouses protect plants from extreme weather, pests, and diseases while allowing for the use of natural light, reducing the need for artificial lighting.
2. How do I choose the right location for my greenhouse?
When selecting a location for your greenhouse, consider factors such as sunlight exposure, wind protection, accessibility, ground conditions, water drainage, privacy, security, and climate. Ensure the location receives at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight, is sheltered from strong winds, is easily accessible, and has good drainage. Additionally, choose a discreet spot to protect your crop and comply with local regulations.
3. What type of greenhouse should I use for growing cannabis?
Several types of greenhouses are suitable for cannabis cultivation, including cold frame greenhouses, hoop houses, polycarbonate greenhouses, glass greenhouses, and geodesic dome greenhouses. Each type has its advantages and disadvantages. Consider factors such as durability, insulation, light transmission, and cost when choosing the right greenhouse for your needs.
4. How do I prepare my greenhouse for cannabis cultivation?
To prepare your greenhouse for cannabis cultivation, ensure proper lighting, temperature control, humidity control, and ventilation. Use high-quality soil or soilless mixes and choose appropriate containers for your plants. Implement a consistent lighting schedule, maintain optimal temperatures, control humidity levels, and ensure adequate air circulation.
5. What are the best strains for greenhouse cultivation?
Choose strains that are well-suited for greenhouse growing and your climate. Indica strains tend to be shorter and bushier, while sativa strains are taller and require more space. Hybrid strains offer a balance of traits from both indica and sativa. Consider using feminized seeds to ensure all plants are female and autoflowering seeds for a shorter growing cycle.
6. What are light deprivation (light dep) techniques, and how do I use them?
Light deprivation (light dep) techniques involve manipulating the light cycle by covering the greenhouse to block out light for part of the day. This simulates the natural light cycles of different seasons, inducing flowering at specific times. To effectively implement light dep techniques, use blackout tarps or lightproof fabrics, maintain a consistent light dep schedule, ensure proper ventilation, and monitor environmental conditions.
7. How do I manage temperature and humidity in a greenhouse?
To manage temperature, use heaters in colder climates and shade cloths, ventilation fans, and evaporative coolers in hot climates. Maintain temperatures between 70-85°F (21-29°C) during the day and 60-70°F (15-21°C) at night. Control humidity by using dehumidifiers, proper ventilation, and adjusting watering schedules. Aim for 60-70% relative humidity during the vegetative stage and 40-50% during the flowering stage.
8. What are some common pests and diseases in greenhouse cannabis cultivation, and how do I prevent them?
Common pests include aphids, spider mites, whiteflies, and caterpillars, while common diseases include powdery mildew, bud rot, and root rot. Prevent pests and diseases by maintaining proper humidity levels, ensuring good air circulation, regularly inspecting plants, using organic pest control methods like neem oil or insecticidal soap, and introducing beneficial insects like ladybugs.
9. How do I harvest and cure cannabis grown in a greenhouse?
Determine harvest time by inspecting trichome color (milky white with some turning amber) and pistil color (turning from white to orange or brown). Use sharp, clean scissors to cut branches or individual buds and trim away large fan leaves and smaller sugar leaves. Dry buds by hanging them upside down in a dark, well-ventilated room for 7-14 days. Cure buds by placing them in airtight glass jars, opening the jars daily to release moisture, and allowing fresh air in for the first 1-2 weeks. Cure for at least 2-4 weeks, though longer curing times can enhance quality.
10. How do I handle common issues in greenhouse cannabis cultivation?
Address temperature fluctuations by using heaters or cooling systems, manage high humidity with dehumidifiers and ventilation, control pest infestations with organic methods and beneficial insects, correct nutrient deficiencies with balanced feeding schedules and soil pH testing, and improve air circulation with oscillating fans and proper ventilation. Regular monitoring and adjustments are key to maintaining a healthy growing environment.
Suggested Articles
;)
;)
;)




 10 Mar 2026
10 Mar 2026  10 min read
10 min read


 June 18, 2024
June 18, 2024 


RESPONSES (0)
No responses yet. Be the first to respond!