Aquaponics for Cannabis: A Revolutionary Growing Method
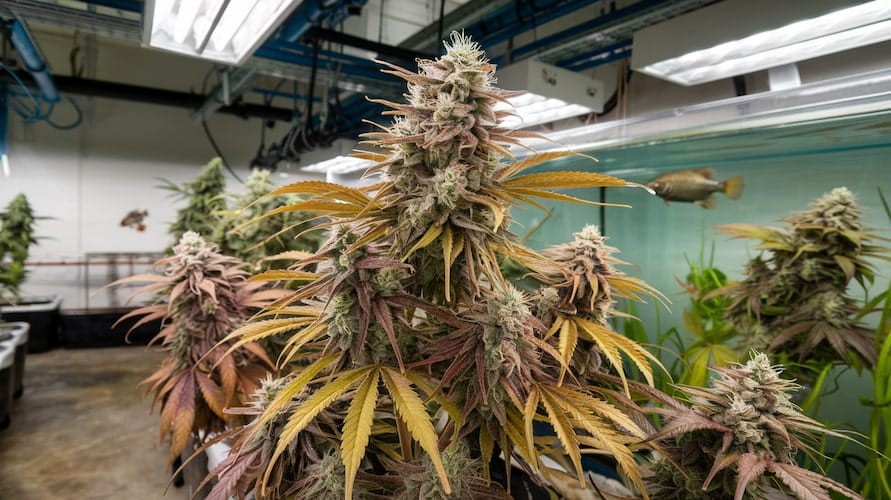

Cannabis cultivation has evolved over the years, incorporating various techniques to boost efficiency, sustainability, and yield. One of the latest trends making waves in the cannabis-growing community is aquaponics—a combination of aquaculture (raising fish) and hydroponics (growing plants in water). This innovative method offers several benefits for both hobbyists and commercial growers.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive deep into aquaponics, explaining how it works, its advantages, and how it can be successfully used to grow top-quality cannabis.
What Is Aquaponics?
Aquaponics is a closed-loop system that mimics a natural ecosystem. In this system, fish waste provides essential nutrients for the plants, while the plants, in turn, clean and filter the water for the fish. This symbiotic relationship reduces the need for chemical fertilizers and conserves water, making it an eco-friendly alternative to traditional soil-based growing.
How Aquaponics Works
In aquaponics, the main components are:
- Fish Tank: This is where fish (commonly tilapia, koi, or goldfish) are kept. The fish excrete waste, primarily in the form of ammonia, which bacteria convert into nitrates.
- Grow Bed: The grow bed holds your cannabis plants. The plants absorb the nitrates, which serve as nutrients, and in turn, clean the water that flows back into the fish tank.
- Biofilter: This is where the magic happens. The biofilter is home to beneficial bacteria that break down fish waste (ammonia) into nitrites and then nitrates, which are safe and beneficial for plants.
- Water Circulation System: A pump continuously cycles water between the fish tank and grow bed, ensuring a steady supply of nutrients for the plants while maintaining clean water for the fish.
This harmonious setup can sustain itself with minimal input while promoting robust cannabis growth.
Benefits of Aquaponics for Cannabis
Aquaponics offers several advantages over traditional soil-based and even hydroponic systems:
1. Eco-Friendly and Sustainable
One of the most significant advantages of aquaponics is its sustainability. It uses up to 90 percent less water than traditional soil-based growing because the water is recirculated. The system requires no chemical fertilizers, reducing the potential for environmental pollution. In addition, it provides a closed-loop system that minimizes waste.
2. Natural Nutrient Source
Instead of relying on synthetic fertilizers, aquaponics uses fish waste as a natural and constant nutrient source for your cannabis plants. The fish excrete ammonia, which is then converted into nitrates by bacteria in the biofilter. These nitrates serve as the primary nutrient for your plants.
3. Reduced Pest Pressure
Growing in an aquaponics system means no soil, which eliminates many of the pests typically associated with soil-based cultivation, such as root aphids and fungus gnats. The absence of soil also minimizes the risk of soil-borne diseases, creating a healthier growing environment.
4. Faster Growth and Higher Yields
Cannabis grown in aquaponic systems often matures faster and produces higher yields compared to traditional soil methods. The constant supply of nutrients and oxygen in the water, combined with optimized growing conditions, encourages vigorous growth.
5. Synergy Between Fish and Plants
The mutually beneficial relationship between the fish and plants reduces the need for manual intervention. As long as the system is maintained properly, both the fish and cannabis plants thrive.
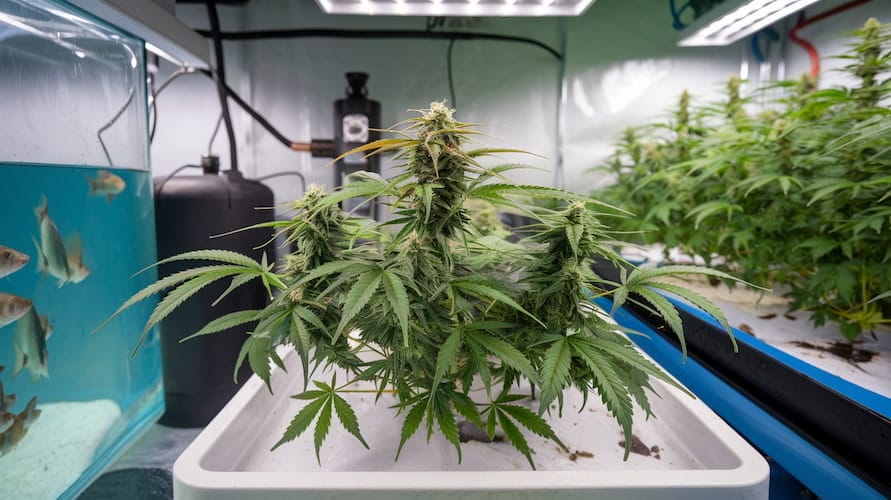

Setting Up an Aquaponics System for Cannabis
Building an aquaponics system for cannabis cultivation requires careful planning. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to set up your system:
Step 1: Choose Your Fish
Not all fish are suitable for aquaponics, especially if you’re growing cannabis. Common choices include:
- Tilapia: These are popular due to their resilience, fast growth rate, and ability to tolerate varying water conditions.
- Koi: Koi fish are hardy and can live for many years. They’re also aesthetically pleasing, making them a great addition to your system.
- Goldfish: Ideal for smaller setups, goldfish are easy to care for and produce plenty of waste to fuel your plants.
Ensure the fish species you choose are legal to raise in your area and can thrive in the environment you’re providing.
Step 2: Set Up the Fish Tank
The size of your fish tank will depend on the scale of your operation. As a general rule, a 1:1 ratio between fish tank volume and grow bed area works well for cannabis cultivation. A larger fish tank supports a higher density of fish, which in turn produces more nutrients for your plants.
Make sure to provide adequate filtration and aeration for the fish. An air pump and water pump are essential for maintaining oxygen levels and ensuring water circulation throughout the system.
Step 3: Design the Grow Bed
Your grow bed will house the cannabis plants, so it needs to be large enough to accommodate the root systems. Media-based grow beds, filled with clay pebbles or gravel, are a popular choice because they offer support to the plant roots and provide a surface for beneficial bacteria to thrive.
Step 4: Install a Biofilter
The biofilter is where the conversion of ammonia to nitrates takes place. It’s critical to have a robust biofilter to ensure that the water remains safe for both fish and plants. In media-based grow beds, the grow medium itself often doubles as a biofilter. However, for larger systems, you may need a separate biofilter to handle the volume of fish waste.
Step 5: Water Circulation System
Your water circulation system will move water between the fish tank, grow bed, and biofilter. A submersible water pump can handle this task, and you’ll also need to set up a gravity-fed system or overflow mechanism to ensure the water flows back into the fish tank.
Maintain a balanced flow rate to ensure the plants receive enough nutrients and oxygen, but not too much that they get waterlogged. Water pumps are typically rated by gallons per hour (GPH), so choose one that suits the size of your system.
Step 6: Monitor Water Quality
Water quality is crucial in aquaponics. You’ll need to monitor parameters such as:
- pH: Cannabis prefers a slightly acidic pH of 5.5 to 6.5. Most fish, on the other hand, thrive at a pH of 6.5 to 7.0. It’s essential to strike a balance between these two preferences.
- Temperature: The optimal water temperature for cannabis is between 65 and 80 degrees Fahrenheit. Fish like tilapia can tolerate a wide range of temperatures, but it’s important to avoid extremes.
- Ammonia and Nitrate Levels: Regular testing for ammonia and nitrate levels will ensure that your system is working correctly. High ammonia levels can harm the fish, while insufficient nitrates will limit plant growth.
Step 7: Plant Your Cannabis
Once the system is set up and your water parameters are stable, it’s time to plant your cannabis. Seedlings or clones can be transplanted directly into the grow bed. Since the plants will have constant access to nutrients, they’ll likely experience rapid growth.
Managing Aquaponics for Cannabis
Successfully managing an aquaponic cannabis system requires a keen eye on various factors. Below are some key management practices:
1. Balancing Fish and Plants
The balance between fish and plants is critical for a successful aquaponics system. Too many fish and not enough plants can lead to ammonia build-up, which is harmful to the fish. Conversely, too many plants and not enough fish will result in nutrient deficiencies for your cannabis.
A good rule of thumb is to have 1 pound of fish for every five to seven gallons of water, though this can vary based on the species of fish and the size of your grow bed.
2. Nutrient Management
While fish waste provides most of the nutrients cannabis needs, you may still need to supplement with minerals like iron, potassium, and calcium, especially during the flowering stage when cannabis plants demand more nutrients. Be sure to use supplements that are safe for fish to avoid harming your aquatic friends.
3. Pest Control
Although aquaponics significantly reduces the risk of pests, it’s not entirely pest-free. Some common cannabis pests, such as spider mites, can still find their way into your grow room. To manage pests without harming the fish, consider using organic pest control methods like neem oil or introducing beneficial insects like ladybugs.
4. Light Management
Lighting plays a crucial role in cannabis cultivation. In an aquaponic system, you’ll need to provide the same type of grow lights you would use in a hydroponic or soil-based grow. LED lights are a popular choice because they’re energy-efficient and produce less heat, which helps maintain optimal water temperatures for the fish.
Ensure that your cannabis plants receive 18 hours of light during the vegetative stage and 12 hours during the flowering stage.
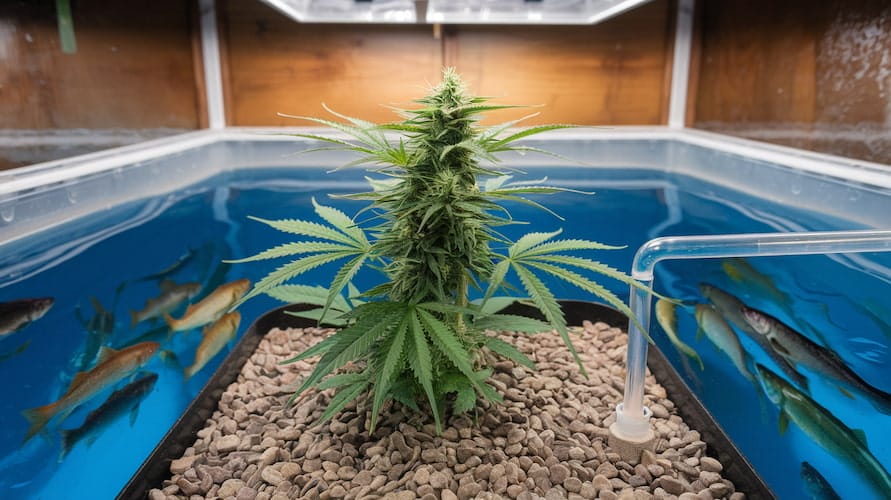

Common Challenges in Aquaponics for Cannabis
Aquaponics may sound like the perfect growing solution, but it comes with its own set of challenges. Let’s explore some of the common issues that may arise in an aquaponics cannabis setup and how to address them.
1. Balancing Nutrient Levels
One of the most significant challenges in aquaponics is maintaining a balance between the nutrient needs of both fish and plants. Fish produce waste that turns into ammonia, which is then converted into nitrates by bacteria. However, cannabis plants, especially during flowering, require higher concentrations of nutrients than fish waste alone can provide.
Solution: You can supplement the system with additional organic nutrients like seaweed extract, iron chelates, or potassium sulfate. These supplements should be fish-safe, so ensure that any additives you use do not disrupt the aquatic life in your system.
2. pH Fluctuations
Maintaining a stable pH level is crucial for both fish and cannabis plants. Cannabis prefers a slightly acidic environment (pH 5.5-6.5), while many fish species, such as tilapia, prefer a more neutral pH (6.5-7.5). Fluctuations in pH can affect nutrient absorption in plants and the overall health of the fish.
Solution: Use pH adjusters that are safe for aquaponics systems. You may need to add small amounts of pH-lowering solutions like phosphoric acid or pH-raising substances like calcium carbonate. Monitoring the pH daily and making gradual adjustments is key to keeping both your fish and plants happy.
3. Temperature Control
Cannabis plants and fish require specific temperature ranges for optimal growth. The challenge is that cannabis thrives at different temperatures than most fish. For instance, cannabis grows best in temperatures between 68 and 77 degrees Fahrenheit, while fish like tilapia prefer warmer water, typically 75 to 85 degrees Fahrenheit.
Solution: If you’re growing cannabis in a colder environment, use water heaters for the fish tank to maintain proper temperatures. Conversely, you can employ cooling methods, such as fans or an air conditioning unit, to keep the grow room cool enough for your cannabis plants. Maintaining good air circulation can also help balance the temperatures for both fish and plants.
4. Water Quality Management
Water quality is critical in aquaponics. Cannabis requires clean, nutrient-rich water, and fish need an oxygen-rich, ammonia-free environment. If the water is not properly filtered and circulated, it can result in oxygen deficiency for fish, nutrient imbalances for plants, or even dangerous levels of ammonia.
Solution: Use high-quality filtration systems and biofilters to ensure that water stays clean and oxygenated. Regular water testing for ammonia, nitrate, and oxygen levels can help you stay ahead of potential issues. Adding a backup aeration system can also ensure the fish get enough oxygen even in case of a power outage.
5. Fish Health Issues
Fish health is paramount in an aquaponic system, as sick or stressed fish may stop producing waste, leading to a lack of nutrients for your cannabis plants. Overcrowding, poor water quality, or diseases can compromise fish health.
Solution: Avoid overstocking your fish tank and ensure regular water changes. If diseases arise, it’s best to consult a fish veterinarian for treatment options. You can also add fish-safe antibiotics or other medications to the water, but be cautious to avoid disrupting the aquaponic ecosystem.
Best Practices for Aquaponics Cannabis Growing
To overcome these challenges and maintain a thriving aquaponics cannabis setup, follow these best practices:
1. Start Small
If you’re new to aquaponics or cannabis cultivation, it’s advisable to start with a small system. This allows you to learn the intricacies of the method without the high stakes of a large-scale setup. Starting small also makes it easier to manage nutrient levels, water quality, and fish health.
2. Choose Hardy Fish and Plants
Selecting hardy fish like tilapia and resilient cannabis strains like Northern Lights or White Widow can increase your chances of success. These species are more forgiving to fluctuations in water quality or nutrient levels, making them ideal for beginners.
3. Regular Monitoring
An aquaponics system requires constant monitoring of several factors, including water temperature, pH, nutrient levels, and oxygen content. Investing in automated systems that monitor and regulate these variables can take some of the pressure off, but it’s still essential to check on your system regularly.
4. Proper Lighting and Humidity Control
Ensure that your grow lights are set up for the proper light cycles (18 hours on for vegetative growth and 12 hours on for flowering). Be aware that aquaponics systems can create more humidity than soil-based grows, so invest in dehumidifiers or proper ventilation to prevent mold or mildew from affecting your plants.
5. Backup Power
Aquaponics systems rely on constant water circulation and aeration for both the plants and fish. In the event of a power outage, your system could crash, resulting in oxygen depletion for the fish and stagnant water for the plants. Having a backup generator or battery-powered air pump can help avoid these issues.
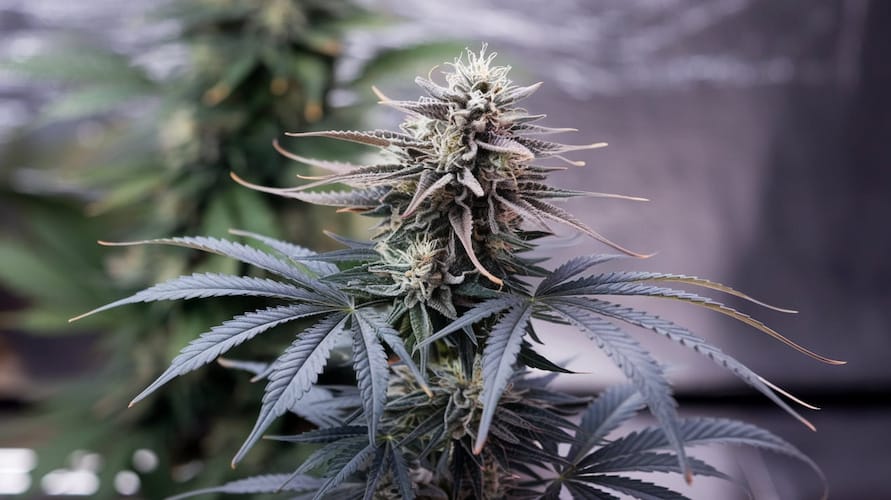

How To Maximize Cannabis Yield in Aquaponics
Once you’ve mastered the basics, the next step is optimizing your aquaponics setup to maximize your cannabis yield. Here’s how you can push your system to the next level:
1. Optimize Nutrient Availability
Although fish waste provides many of the nutrients cannabis needs, plants often require additional phosphorus, potassium, and calcium during flowering to support bud growth. Introduce supplements specifically designed for aquaponics systems to ensure your plants have the right nutrient balance at every stage.
2. Train Your Plants
To maximize yield in your aquaponics system, use training techniques like low-stress training (LST), Screen of Green (ScrOG), or topping. These methods encourage cannabis plants to produce more bud sites and spread their canopy for optimal light exposure.
3. Monitor Water and Light Cycles
Cannabis plants grown in aquaponics benefit from consistent light cycles and stable water conditions. Make sure your lighting schedule is precise, and consider using timers for your grow lights to automate the process. Additionally, keep the water temperature stable to avoid stressing both the plants and the fish.
4. Maximize Plant Density
Since aquaponics systems allow for vertical growing, you can maximize the available space in your grow room by incorporating tiered systems. This vertical space optimization can increase the number of cannabis plants you can cultivate without needing a larger footprint for your grow bed.
Aquaponics for Cannabis: Conclusion
Aquaponics is an exciting, sustainable, and efficient method of growing cannabis that offers numerous benefits to both small-scale hobbyists and large-scale commercial growers. While it requires careful management of both fish and plants, the rewards of healthier plants, faster growth, and higher yields make it an attractive option for cannabis cultivators.
By maintaining balance in the system, providing the right nutrients, and ensuring optimal conditions for both the fish and the cannabis plants, you can enjoy a successful aquaponics grow and produce top-quality cannabis with minimal environmental impact. Whether you’re an experienced grower looking to experiment with new techniques or a beginner seeking a more sustainable method, aquaponics offers a unique opportunity to revolutionize your cannabis cultivation experience.
Now that you know all about aquaponics for cannabis, get your garden started by shopping the collection of regular, feminized, and autoflower cannabis seeds and clones at Seeds Here Now.
FAQs
1. Is aquaponics cannabis cultivation expensive?
Setting up an aquaponics system requires an initial investment for the tanks, pumps, grow beds, and other necessary equipment. However, once the system is up and running, operational costs are relatively low since water and nutrient use is highly efficient.
2. Can I grow cannabis indoors with aquaponics?
Yes, aquaponics is highly adaptable for both indoor and outdoor cannabis cultivation. Indoor systems give you more control over environmental factors like temperature, humidity, and light, which can lead to more consistent yields.
3. Do I need to be an expert in fish care to start aquaponics?
While it’s helpful to have some basic knowledge of aquaculture, you don’t need to be an expert. Many beginners start with hardy fish like tilapia, which are more forgiving of slight fluctuations in water quality. As long as you monitor the system regularly and maintain proper water conditions, your fish should thrive.
4. How often do I need to feed the fish in an aquaponics system?
Fish should be fed once or twice a day, depending on the species and the size of the system. It’s essential not to overfeed, as uneaten food can lead to water contamination and ammonia spikes, harming both the fish and plants.
5. Can I grow organic cannabis with aquaponics?
Yes, aquaponics is a natural growing method, and if you avoid using synthetic additives, you can grow organic cannabis. Many aquaponic systems are considered organic by default since they rely on natural biological processes to provide nutrients to the plants.

Subscribe to our newsletter
Your dream garden is a subscription away! Join our email list and enter our Monthly Seed Giveaway. Imagine the possibilities each month as you await your chance to win.
By clicking the "Subscribe now" button, I agree and accept the privacy policy of Search Engine Journal.
Suggested Articles
;)
;)
;)




 21 May 2025
21 May 2025  7 min read
7 min read


 October 23, 2024
October 23, 2024 


RESPONSES (0)
No responses yet. Be the first to respond!