Cannabis Plant Anatomy: A Closer Look
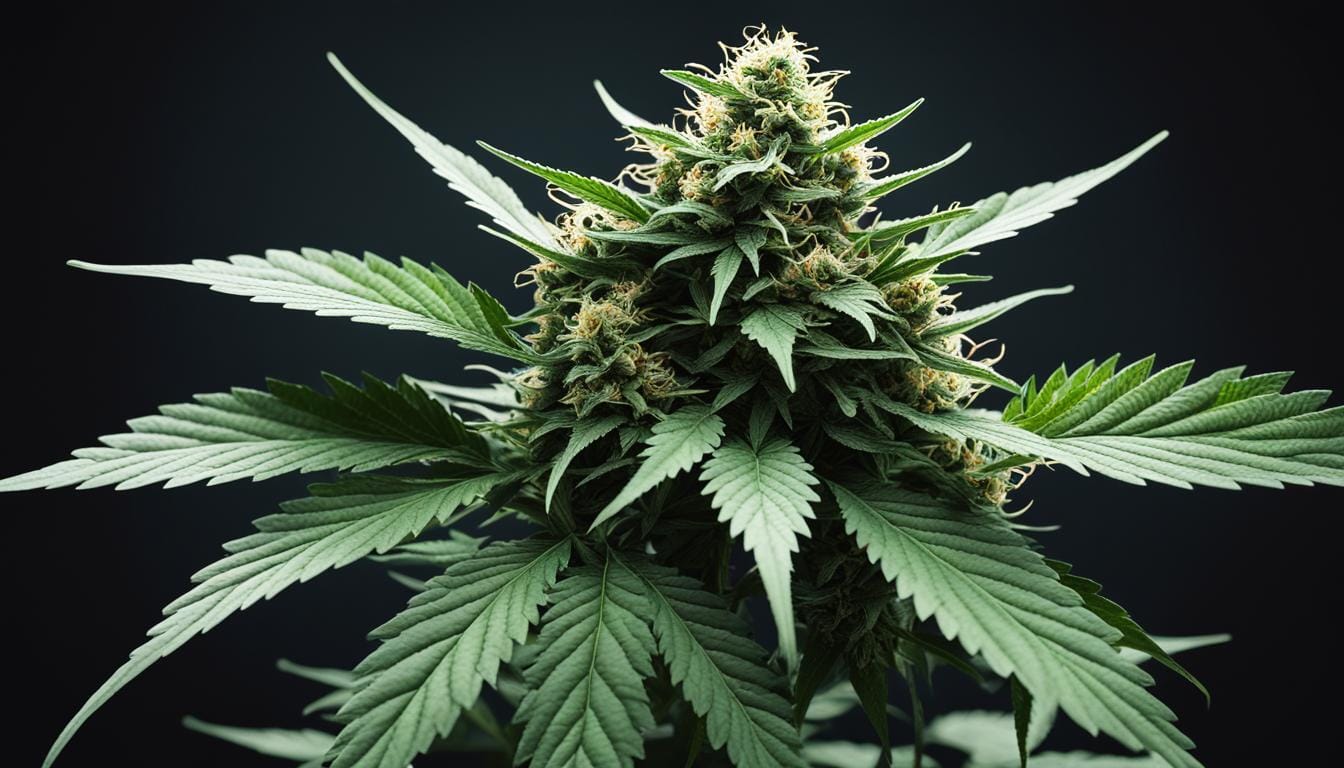

The intriguing world of Cannabis plant anatomy extends far beyond the ubiquitous imagery of its leaf to encompass a structural complexity that is both essential and compelling. For aficionados and cultivators alike, understanding the structure of cannabis plants offers invaluable insights into nurturing them to their full potential. With each part playing a critical role—from the deep-reaching roots to the resinous flowers—marijuana plant anatomy is a fascinating topic that marries botanical science with horticultural expertise.
So, without further ado, let’s dive into the fascinating world of cannabis plant anatomy.
Key Takeaways
- A detailed understanding of cannabis anatomy is essential for optimal cultivation
- From roots to flowers, every part of the cannabis plant plays a crucial role in growth and potency
- Botanical science and horticulture intersect in the study of marijuana plant anatomy
- Appreciation for the structure of cannabis promotes better quality in harvests
- Insights into cannabis anatomy inform responsible and effective plant care
Understanding Cannabis Plant Anatomy
The intricate anatomy of cannabis is essential to the plant’s lifecycle, with each component playing a specific role that affects the plant’s growth, potency, and ability to reproduce. By delving into cannabis plant morphology, cultivators and enthusiasts can gain insights into its unique structure.
The Basics of Marijuana Plant Structure
Understanding the parts of a cannabis plant is fundamental in the world of cultivation. The cannabis plant comprises distinct parts such as the roots, stems, leaves, flowers, and seeds—each of which has its importance and function. These elements work together in symmetry to support the plant’s growth and development.
Importance of Studying Cannabis Morphology
The study of cannabis plant morphology not only provides a blueprint for identifying the various parts of a cannabis plant but also imparts critical insights that are vital for effective cultivation. Knowledge of the anatomy helps in recognizing signs of health and distress, managing nutrient intake, and optimizing the conditions for each stage of the plant’s life cycle. This understanding ensures that every decision made in the cultivation process is informed and precise, potentially leading to a more bountiful and successful harvest.
Delving Into the Cannabis Seed
The journey of a cannabis plant begins with the tiny, yet immensely significant cannabis seed. Rich in potential, every seed encapsulates the future of a marijuana plant, marking the commencement of a cultivator’s quest toward a bountiful harvest. Let’s take a closer look at the outer and inner intricacies of these remarkable seeds.
The Exterior: Appearance and Texture
The robust exterior of cannabis seeds is noteworthy. Each seed is enveloped in a protective shell, baring distinctive “tiger stripes” or mottled patterns that serve as a visual indicator of their identity. The texture is typically hard and smooth, an evolutionary trait that safeguards the vital components within.
Inside the Seed: Embryo and Germination Process
Breaking through this tough exterior reveals the embryo, the nascent beginning of a marijuana plant. This embryo, a prelude to the germination of cannabis, is an assembly of essential parts: the radicle that will become the primary root, the cotyledons or “seed leaves,” and the apical tip, from which the stem will develop. Given the right conditions of moisture and temperature, germination commences, and a seedling emerges, setting the foundation for a healthy and robust cannabis plant.
| Seed Component | Function | Importance in Plant Development |
|---|---|---|
| Exterior Shell | Protection of embryo | Ensures the integrity of the marijuana plant’s genesis |
| Radicle | Primary root structure | Initial anchor and nutrient uptake for the seedling |
| Cotyledons | First leaves to emerge | Performs early photosynthesis, critical for initial growth |
| Apical Tip | Originates the main stem | Supports vertical growth and dictates the future structure |
Note: Each cannabis seed holds a promise—a testament to the intricate life cycle that awaits cultivation.
Exploring the Root System of Cannabis Plants
The intricate root network of the cannabis plant lays the foundation for its overall health and productivity. A robust root system is crucial across all cannabis plant growth stages, ensuring efficient nutrient uptake and stabilization for the burgeoning plant. A proper understanding of the root structures can lead to improvements in cannabis cultivation techniques, thus maximizing the potential of each crop.
Types of Roots and Their Functions
The cannabis plant root system is composed of several key elements, each of which carries out vital roles for plant development:
- Tap Root: The primary root that drives deep into the soil to anchor the plant and access water from further below the surface.
- Fibrous Roots: These spread out from the tap root in a dense network and are important for absorbing nutrients and water closer to the soil’s surface.
- Adventitious Roots: Roots that may grow from parts of the plant other than the root system, like stems or leaves, contributing to the plant’s stability and nutrient uptake.
Role of Roots in Plant Health and Yield
The roots play a non-negotiable part in directing the trajectory of a plant’s growth and yield. They are not only critical in the absorption of essential nutrients and water but also have a profound impact on the plant’s resilience to stress and overall cannabis plant growth stages. By optimizing the conditions for root development, cultivators can significantly enhance the vigor of their cannabis plants.
| Root Type | Primary Function | Contribution to Cannabis Cultivation |
|---|---|---|
| Tap Root | Stabilization and water access | Ensures plant security, allowing for upward growth and access to deep water reserves |
| Fibrous Roots | Nutrient absorption | Increases the nutrient intake that fosters plant health during vegetative and flowering stages |
| Adventitious Roots | Additional support and nutrient absorption | Improves plant stability and has the potential to uptake nutrients if primary roots are damaged |
The Vegetative Powerhouse: Stems and Nodes
At the heart of cannabis plant structure, the stems and nodes play pivotal roles in the life cycle and overall health of the plant. It’s imperative to understand the specific functionalities of these components to appreciate their significance in cultivation and growth.
Physiology of the Cannabis Stem
The cannabis stem serves as more than a mere pillar for the plant’s leaves and branches; it is a superhighway for the transport of vital nutrients and water. Its rigid structure ensures the cannabis plant maintains its upright stance, allowing for optimal light absorption, a crucial factor in the growing process.
Nodes: The Key to Growth and Development
The nodes are points on the cannabis stem where leaves and branches form and extend outward. These are the critical junctures that give rise to the lush foliage of the cannabis plant, and careful observation of node development can often provide growers with insights into the plant’s health and vigor.
Cannabis stem and nodes are not merely structural; they’re indicative of the plant’s potential for bushiness, yield, and flower production.
Let’s examine the various functions of cannabis nodes and how they contribute to the anatomy of marijuana plants:
| Node Function | Description | Significance in Growth |
|---|---|---|
| Leaf/Bud Site | Point where leaves and potential buds form | Directly impact the quantity and distribution of the plant’s foliage and buds |
| Branching Out | Origin for new branches | Influences the plant’s structure and its ability to sustain a plentiful harvest |
| Auxin Production | Auxins are hormones produced at nodes that regulate plant growth | Controls the stretching between nodes, affecting overall plant size and light exposure |
| Cloning | Cuttings taken from nodes can be used to clone plants | Enables growers to replicate successful phenotypes for consistent quality |
In cannabis cultivation, recognizing the importance of proper stem and node care can lead to the development of strong, healthy marijuana plants capable of bearing robust yields. The cannabis stem and nodes are indeed foundational elements in the cannabis plant structure that deserve the utmost attention from cultivators.
Cannabis Leaves and Petioles: Nature’s Solar Panels
The anatomy of cannabis leaves makes them one of the most recognizable and crucial aspects of cannabis plant morphology. Acting as efficient solar panels, they capture sunlight to facilitate photosynthesis, the process through which the plant converts light energy into the chemical energy it needs to grow. A deeper understanding of the parts of a cannabis plant, specifically the leaves and their petioles, can give us insight into the plant’s overall health and vitality.
Leaf anatomy varies between cannabis species and strains, providing clues to their genetic lineage and optimal growing conditions. For instance, the number of leaflets can range from as few as three in some indica strains to as many as thirteen in sativa varieties. Moreover, the color and shape of the leaves may indicate nutrient deficiencies or environmental stressors affecting the plant. These variations are important for cultivators and enthusiasts alike, as they can influence decisions on care and cultivation practices.
Each leaf and its petiole serve as critical components in the health and efficiency of the cannabis plant. The petioles, often overlooked, hold the secret to the leaf’s orientation towards the light—maximizing energy absorption and influencing the rate of growth and development.
- Serrated edges: Maximize the surface area for sunlight absorption.
- Compound structure: Increases the efficiency of light capture.
- Petioles: Connect the leaf to the stem, allowing for flexibility and optimal orientation towards the light source.
By observing the leaf and petiole structures, one can gain insight into the cannabis plant’s overall well-being. Leaf checks should become a regular part of plant care, as they can reveal early signs of distress, allowing for timely intervention. Below is a comparison of typical characteristics found in the leaves of indica and sativa cannabis strains:
| Characteristic | Indica | Sativa |
|---|---|---|
| Leaflet Count | Fewer (5-7) | More (7-13) |
| Leaflet Shape | Broad | Narrow |
| Leaf Color | Darker Green | Lighter Green |
| Leaf Size | Larger | Smaller |
| Plant Size | Short and Bushy | Tall and Slender |
In essence, the anatomy of cannabis leaves is a testament to the plant’s adaptability and resilience. Understanding how these structures function not only deepens our appreciation for the cannabis plant but also enhances our ability to cultivate it effectively.
Elegant Complexity: Cannabis Plant Flowers
The cannabis plant stands as a testament to nature’s complexity, particularly when examining the anatomy of marijuana buds and flowers. These biological marvels go beyond mere aesthetic appeal and hold the key to the plant’s reproductive success as well as the potency and therapeutic effects sought after by consumers and patients alike.
Understanding the anatomy of the cannabis plant requires a deep dive into the composition of its flowers. In this exploration, the distinction between male and female plants becomes evident, with each contributing to the lifecycle in unique ways. Female plants, in particular, boast the development of buds teeming with cannabinoids.
Sex Identification: Male vs Female Flowers
Being dioecious, cannabis plants present two sexes: male, with their pollen sacs designated for fertilization, and female, with their sticky stigmas ready to catch pollen. Cannabis plant reproductive organs are fascinating for their crucial roles; growers must identify and often isolate male plants to prevent pollination, ensuring that female plants produce the sinsemilla buds valued for medical and recreational use.
The Cola, Pistil, Bracts, and Calyx in Flower Development
At the zenith of marijuana plant anatomy, the female plant’s cola refers to the dense cluster of buds that develop during the flowering stage. The pistil, visually distinct with its hair-like strands, indicates a plant’s readiness to be pollinated. Bracts and calyxes provide protective enclosures for the developing seeds, but in their absence, they swell with the resin rich in cannabinoids and terpenes. Grasping this complex yet elegant structure is vital for both botanists and cultivators aiming to understand and harness the full potential of the cannabis plant.
Cannabis Trichomes: The Crystals of Potency
The mystique surrounding cannabis trichomes is not just about their glittering appearance; these tiny structures are a defining feature of the anatomy of cannabis leaves and buds. Trichomes are a testament to the evolutionary mastery of the cannabis plant, serving as guardians of the plant’s most precious compounds. To aficionados and connoisseurs, trichomes announce the robustness of cannabinoid and terpene profiles within cannabis flowers. Let’s unravel the mystery of trichomes and their crucial role in cannabis potency.
Function and Composition of Trichomes
Resembling small, glassy hairs, trichomes are predominantly situated on cannabis buds and leaves. They are the powerhouses producing cannabinoids such as THC and CBD, as well as various terpenes and flavonoids that give each strain its unique fragrance and flavor. The role of trichomes extends beyond production to plant protection, safeguarding against UV rays and pests while reducing the risk of fungal diseases.
Harvesting and Utilization in Cannabis Products
For cultivators, the lifecycle of trichomes is the yardstick for determining the optimal harvest time. Recognizing that clear trichomes suggest immaturity and amber ones indicate excessive maturity, farmers strive for the milky white stage indicating peak potency. Post-harvest, trichomes are pivotal in the creation of concentrates, oils, and tinctures. These compounds distill the essence of cannabis, promising enhanced therapeutic and recreational experiences.
Given their importance, the following table presents key attributes and considerations associated with the harvesting and refining process of cannabis trichomes:
| Trichome Attribute | Harvest Consideration | Implication for Products |
|---|---|---|
| Color and Clarity | Milky white indicates peak maturity for harvest | Ensures maximum potency in final product |
| Resin Consistency | Sticky and gooey texture preferred | Indicative of rich cannabinoid and terpene profiles |
| Density | Abundant trichome coverage desired | More trichomes means a greater yield of concentrates |
A deeper appreciation for the cannabis trichomes not only enhances our understanding of the plant’s biology but it also informs the cultivation and extraction practices that lead to high-quality cannabis products. By respecting the intricate anatomy of cannabis leaves and flowers, we can elevate both the science and the art of cannabis consumption.
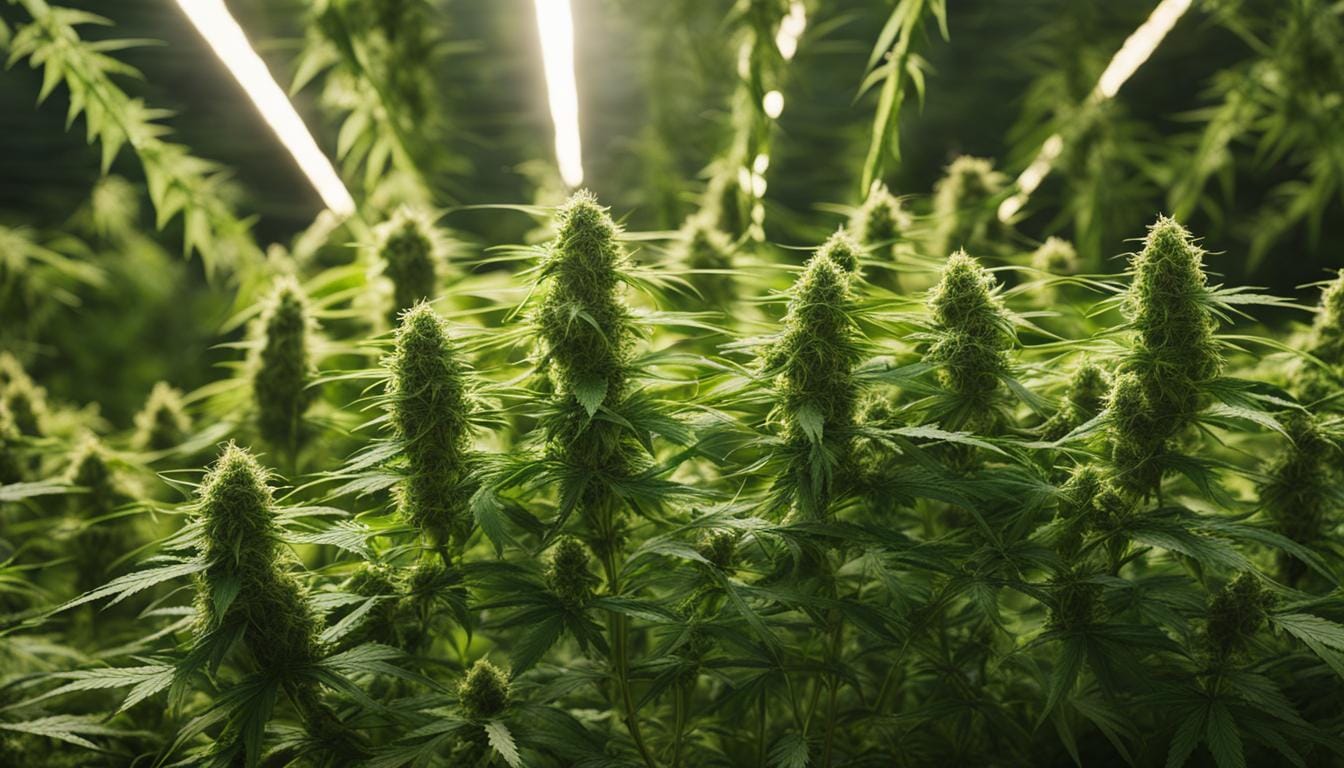

The Reproductive Game: Understanding Cannabis Plant Reproductive Organs
In the complex world of cannabis cultivation, the plant reproductive organs are both a source of fascination and a focal point for growers. These tiny yet powerful structures oversee gene propagation and play a vital role in the quality of the final harvest. Gender distinction among cannabis plants is pivotal as it steers the cultivation process, influencing everything from pollination to the ultimate potency of the crop.
Towards the later growth stages, discerning the sex of a plant becomes critical. Male plants, with their pollen sacs, are typically separated from females to avoid pollination unless seed production is the goal. On the other hand, female plants, particularly those that remain unfertilized, known as “sinsemilla”, are highly prized for their rich cannabinoid profiles. It’s during the flowering phase that these differences become most apparent.
A deeper understanding of these reproductive components not only aids in recognizing the sex of cannabis plants but also allows growers to influence the reproductive processes to optimize yield and quality. Here, in an easy-to-follow format, is a rundown of the primary reproductive organs found in both male and female cannabis plants:
- Male Organs (Staminate): Consist of stamens with anthers that release pollen.
- Female Organs (Pistillate): Comprise stigmas, bracts, and ovaries, which are the crucial elements for producing seeds when fertilized.
For growers aiming for high-quality, potent cannabis, it’s all about timing and observation. As plants transition from vegetative growth to flowering, careful monitoring ensures that male plants can either be isolated or removed completely to protect the sinsemilla integrity of the female plants. This strategic maneuver is integral for those looking to harness the plant’s maximum potential, particularly in generating high-grade, cannabinoid-rich flowers.
The intersection of anatomy and the growth cycle is where expert cultivators make their mark, using their knowledge of cannabis plant reproductive organs and growth stages to influence their cultivation strategies—their secrets rooted deeply in the botany of cannabis.
Cannabis Plant Anatomy and the Growth Stages
Understanding the life cycle of the cannabis plant is as important as knowing its physical structure. Similar to a well-orchestrated symphony, each growth stage harmonizes with specific environmental cues that facilitate its development from a tiny seedling to a thriving plant ready for harvest.
From Seedling to Flowering: Tracing the Life Cycle of Cannabis
The life cycle of cannabis encompasses several distinct stages: germination, seedling, vegetative, and flowering. Each phase is characterized by unique changes in the cannabis plant structure, requiring precise conditions to flourish.
Cultivation Insights: Optimal Conditions for Each Stage
To maximize the health and vigor of cannabis plants, it’s essential to appreciate the nuances of environment and care. We distill the art of growth into a table highlighting optimal conditions tailored to bolster the cannabis plant through its pivotal stages:
| Growth Stage | Light | Temperature | Humidity | Nutrients |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Germination | Indirect, gentle light | 70-85°F (21-29°C) | 70-90% | Low – Start with a light nutrient solution if necessary |
| Seedling | 14-16 hours of light per day | 68-77°F (20-25°C) | 65-70% | Light nutrient mix, progressively increasing |
| Vegetative | 16-18 hours of light per day | 70-85°F (21-29°C) | 40-70% | Increased nitrogen for foliage growth |
| Flowering | 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness | 65-80°F (18-26°C) | 40-50% | Reduced nitrogen, higher phosphorus and potassium |
By adhering to these guidelines, cultivators can ensure their cannabis plants reach each developmental milestone with the vigor needed to thrive. Towards the end of the flowering stage, plants will exhibit dense clusters of trichome-rich buds, signifying readiness for the harvest, the culmination of tireless efforts, and meticulous adherence to the plant’s anatomical needs.
Conclusion
Cannabis plant anatomy is a mosaic of biological wonder, integral to the understanding and cultivation of this fascinating plant. Within its seeds lie the quiet promise of growth; the roots anchor and stretch forth in search of sustenance; and the stems ascend, creating a labyrinth of nodes that mark the passage of energy and life. With each leaf absorbing sunlight and every flower budding with potential, the anatomy of marijuana is a testament to the intricate dance of nature’s designs.
For those with a penchant for horticultural ventures or a curiosity sparked by the marijuana plant anatomy, understanding the plant’s structure is nothing short of crucial. It offers insight into what the plant requires at every phase, from germination to the flowering stage, ensuring that each cultivator can achieve bountiful harvests enriched with cannabinoids and terpenes.
This exploration into cannabis anatomy transcends mere interest; it fosters a holistic grasp of growth patterns and environmental needs that are invaluable for anyone looking to flourish within the ever-evolving realm of cannabis cultivation. Undoubtedly, the wisdom gleaned from these natural frameworks sow the seeds for future innovation and success in the industry.
FAQ
What are the key parts of a cannabis plant?
The key parts of a cannabis plant include the roots, stem, leaves, flowers (or buds), and trichomes. Each part plays a significant role in the plant’s growth and development.
How do cannabis seeds germinate?
Cannabis seeds germinate when exposed to the right conditions of moisture, warmth, and light. The seed’s outer shell cracks open, allowing the radicle (the embryonic root) to emerge, followed by the cotyledons (the first leaves).
What is the function of the cannabis plant’s root system?
The root system anchors the plant, absorbs water and nutrients from the soil, and stores energy. It’s a critical component for the plant’s overall health and directly impacts its yield and potency.
Why is the stem important in the marijuana plant’s structure?
The stem acts as the main support for the plant, assisting in transporting nutrients and water from the roots to the leaves and flowers. It also houses nodes, where leaves and branches develop, crucial for growth patterns.
What role do cannabis leaves play?
Cannabis leaves are essential for photosynthesis, the process by which the plant converts light into energy. They also play vital roles in respiration and transpiration, necessary for the plant’s metabolic processes.
How can I tell the difference between male and female cannabis plants?
Male cannabis plants develop pollen sacs, while female plants grow pistils and produce flower buds. Identifying the sex is critical for cultivation, depending on whether seed production or flower harvest is the goal.
What is a cola on a cannabis plant?
A cola is a cluster of buds that grow tightly together at the top of a cannabis plant’s branches. It’s usually the most cannabinoid-rich part of the plant and is highly sought after by cultivators for its potency.
What are trichomes and why are they important?
Trichomes are tiny, crystal-like structures on the surface of cannabis buds that produce and store resins rich in cannabinoids and terpenes, contributing to the plant’s aroma, flavor, and potency. They’re critical for both plant defense and consumer experience.
What conditions are needed for each growth stage of a cannabis plant?
During the seedling stage, gentle light and moisture are crucial. In the vegetative stage, the plant requires more intense light and nutrients to grow. During the flowering stage, the plant needs specific light cycles, typically 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness, along with appropriate nutrients to develop buds.
How does understanding cannabis plant anatomy help in cultivation?
Knowing the anatomy of the cannabis plant aids cultivators in providing the right conditions and care at each growth stage. It helps diagnose and address issues, ensures proper pruning and training, and assists in identifying the right time to harvest for optimal potency.
Suggested Articles
;)
;)
;)





 24 Feb 2026
24 Feb 2026  7 min read
7 min read


 January 09, 2024
January 09, 2024 


RESPONSES (0)
No responses yet. Be the first to respond!