The Complete Science Behind Cannabinoids: How They Work in Your Body (2025 Guide)
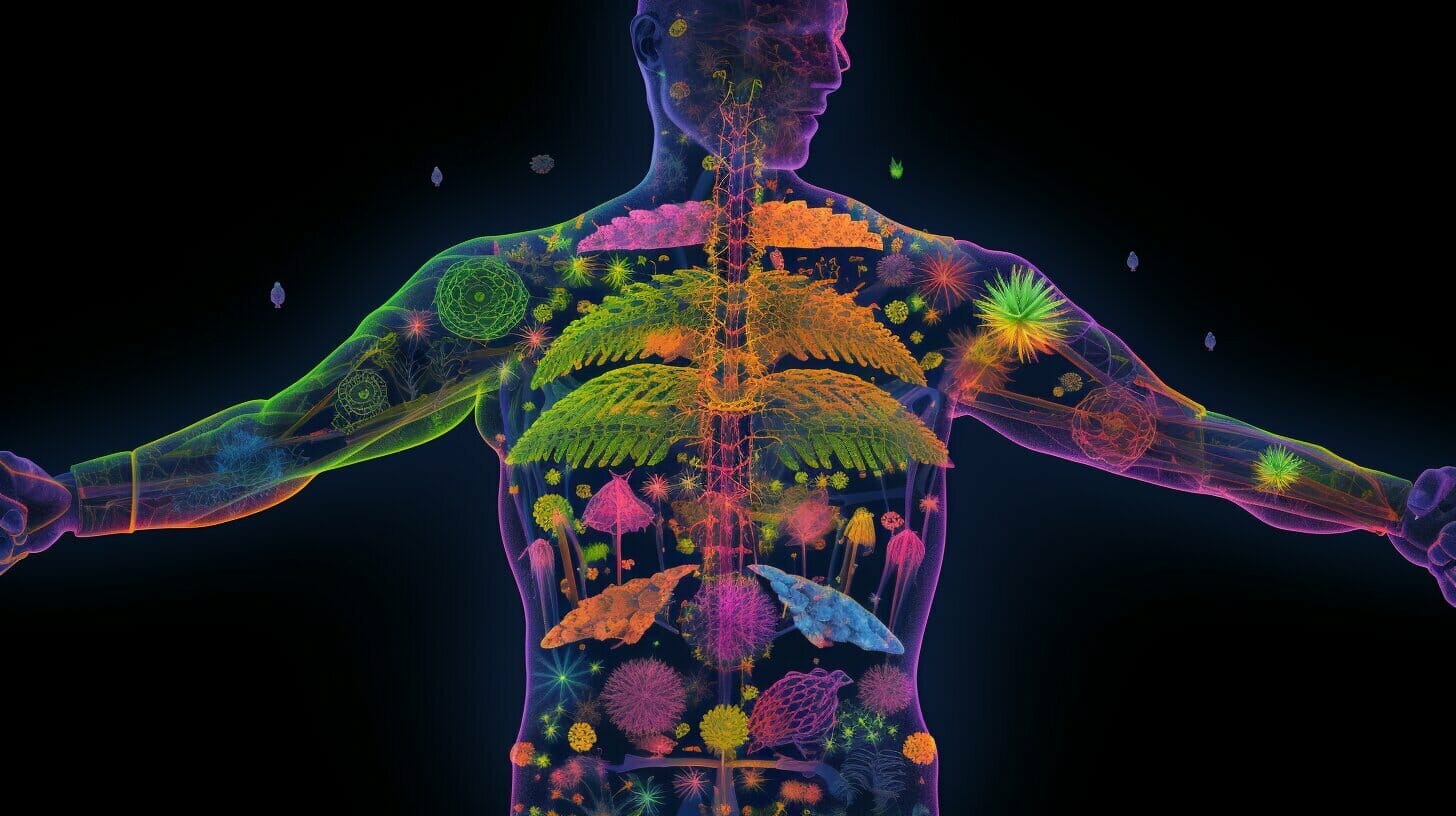
<p>Understanding Cannabinoids: The Breakthrough Compounds Transforming Medicine</p>
<p><strong>Bottom Line:</strong> Cannabinoids are naturally occurring compounds that interact with your body’s endocannabinoid system to regulate pain, inflammation, mood, sleep, and numerous other physiological functions. Recent 2025 research reveals these molecules hold unprecedented therapeutic potential while requiring careful consideration of dosage, timing, and individual factors.</p>
<p>Cannabinoids represent one of the most fascinating areas of modern medical research. These complex molecules, primarily found in the Cannabis sativa plant, have revolutionized our understanding of how the human body maintains balance and responds to therapeutic interventions.</p>
<p>What makes cannabinoids unique? Unlike traditional pharmaceuticals that target specific symptoms, cannabinoids work with your body’s existing regulatory systems to restore natural balance — a process scientists call homeostasis. Understanding these compounds is crucial whether you’re interested in exploring <a href=”https://seedsherenow.com/product-category/feminized”>feminized cannabis seeds</a> for cultivation or learning about therapeutic applications.</p>
<h2>The Cannabinoid Family: More Than Just THC and CBD</h2>
<p>Scientists have identified more than 125 distinct cannabinoids in the cannabis plant, each with unique properties and potential benefits. These compounds work synergistically in what researchers call the “entourage effect,” where multiple cannabinoids enhance each other’s therapeutic properties. For those interested in <a href=”https://seedsherenow.com/what-are-terpenes-and-why-do-i-care/”>cannabis terpenes</a> and their interactions, these aromatic compounds also play crucial roles alongside cannabinoids.</p>
<h2>The Endocannabinoid System: Your Body’s Master Regulatory Network</h2>
<p>When you consume cannabinoids, they bind to these receptors like keys fitting into locks. This interaction triggers a cascade of cellular responses that can:</p>
<ul>
<li>Modulate neurotransmitter release</li>
<li>Regulate inflammation</li>
<li>Influence pain perception</li>
<li>Affect mood and anxiety</li>
<li>Control appetite and metabolism</li>
<li>Regulate sleep-wake cycles</li>
</ul>
<h2>Therapeutic Applications: Evidence-Based Benefits of Cannabinoids</h2>
<p>CBD’s anti-anxiety effects are largely due to interactions with serotonin receptors, a point well-supported by <a href=”https://www.projectcbd.org/”>Project CBD’s</a> database. Cannabinoids like CBD and THC also target vanilloid receptors for pain modulation and interact with PPARγ receptors to regulate metabolism.</p>
<h2>Safety Profile and Considerations: Understanding Risks and Benefits</h2>
<p>Understanding safety considerations is essential for anyone considering cannabinoid therapy. For those interested in cannabis cultivation and growing techniques, knowing about different cannabinoid profiles can help in selecting appropriate strains. Visit our <a href=”https://seedsherenow.com/grow-marijuana-indoors/”>complete cannabis growing guide</a> for detailed insights.</p>
<h2>Dosage and Administration: Optimizing Therapeutic Effects</h2>
<p>Proper dosing is crucial for therapeutic success and safety. Whether you’re exploring <a href=”https://seedsherenow.com/product-category/auto-flower/”>autoflowering cannabis seeds</a> for cultivation or considering therapeutic use, understanding dosage principles is essential.</p>
<h2>Latest Research and Future Directions (2025 Updates)</h2>
<p>Clinical research supported by institutions like <a href=”https://www.leafly.com/news/cannabis-101″>Leafly’s educational resources</a> provides ongoing insights into therapeutic applications and safety profiles.</p>
<h2>Quality and Regulation: Navigating the Cannabinoid Market</h2>
<p>For those interested in understanding quality genetics, exploring <a href=”https://seedsherenow.com/breeders/”>cannabis breeder collections</a> can provide insights into how cannabinoid profiles vary between genetic lines and breeding programs.</p>
<h2>Conclusion: The Promise and Responsibility of Cannabinoid Medicine</h2>
<p>As cannabinoid science continues to evolve, we’re witnessing the emergence of precision medicine approaches that could revolutionize treatment for millions worldwide. The key lies in responsible use, continued research, and evidence-based applications, prioritizing efficacy and safety. For a comprehensive overview of cannabis cannabinoid types, check out our <a href=”https://seedsherenow.com/cbd-vs-cbg-vs-thc-a-understanding-the-cannabinoids-in-your-cannabis-seeds/”>Cannabinoid Guide: THC vs. CBD</a>.</p>
<h2>Frequently Asked Questions About Cannabinoids</h2>
<p>Q: What’s the optimal ratio of THC to CBD?</p>
<p>A: This varies by individual and condition. Common ratios include 1:1 for balanced effects, higher CBD ratios (1:10 to 1:20) for minimal psychoactivity, and THC-dominant ratios for more substantial therapeutic and psychoactive effects. For cultivation insights, our <a href=”https://seedsherenow.com/best-hybrid-cannabis-strains/”>hybrid cannabis strain reviews</a> explore how different genetic profiles affect cannabinoid ratios.</p>
Suggested Articles
;)
;)
;)




 10 Mar 2026
10 Mar 2026  10 min read
10 min read


 December 27, 2023
December 27, 2023 


RESPONSES (0)
No responses yet. Be the first to respond!